PIXet: Difference between revisions
(zacatek manualu) |
(pict test) |
||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
There is no need to install a special driver for the devices. In order to run the software under normal user, it is necessary adjust the permissions of our USB devices in udev system. This can be done by executing the script '''install_driver_rules.sh'''. It is also sometimes necessary to unload the system ftdi_sio driver. Just execute '''rmmod ftdi_sio''' as root in shell before running the software. | There is no need to install a special driver for the devices. In order to run the software under normal user, it is necessary adjust the permissions of our USB devices in udev system. This can be done by executing the script '''install_driver_rules.sh'''. It is also sometimes necessary to unload the system ftdi_sio driver. Just execute '''rmmod ftdi_sio''' as root in shell before running the software. | ||
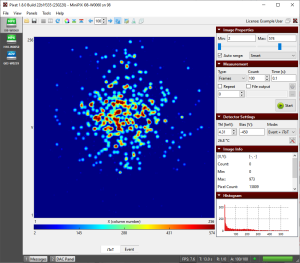
= Main window of PIXet = | |||
== Main window == | |||
The main window the software consists of device sidebar, frame (picture) panel where measured data are visualized, control panel on the right side, toolbar, menu bar, and status panel in the bottom. The panels on the right side can be minimized by clicking on the down arrow in the corresponding panel or can be hidden/shown via menu ''Panels''. | |||
[[File:MainWindow.png|thumb|alt=Pixet Main Window|Pixet Main Window]] | |||
=== Device sidebar === | |||
The device sidebar shows all the connected devices as icons. By clicking on each icon user can open frame panel and control panels of each device. | |||
=== Frame Panel === | |||
The frame panel visualizes measured data (frames). | |||
* '''Zooming area in the frame''' An area in the frame can be zoomed by holding the left mouse button in the frame, dragging the mouse to create a selection rectangle and releasing the mouse button. The area will be zoomed, scrollbars will appear and the X and Y axis will show exact location and size of the zoomed area. The zoomed area can be zoomed further by repeating the steps above. | |||
* '''Moving zoomed area''' The zoomed area can be adjusted by using scrollbars or by dragging the picture with right mouse button. | |||
=== Image Properties panel === | |||
This panel allows for adjusting of color range of the frame. | |||
* '''Min level, Max level''' Adjusts the minimal and the maximal value of the frame that are visible in the frame panel. The values between ''Min level'' and ''Max level'' are then mapped to selected color map. In the case of the gray color map, minimal selected value is black and maximal value is white. To illustrate more clearly, let’s imagine we have a frame 3x3 with values as in the picture below and we set ''Min Level''=1 and ''Max Level''=5. The values under 1 (in this case 0) will not be visible and will be shown in lowest color (black). The values over selected range (in this case 6) will be show in the highest color (white). The rest of the values will be mapped to the 256 colors of the gray map, starting with dark colors for lower values and lighter colors for greater values. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|5 | |||
|1 | |||
|0 | |||
|- | |||
|3 | |||
|4 | |||
|1 | |||
|- | |||
|5 | |||
|6 | |||
|2 | |||
|} | |||
* '''Auto range''' When the auto range checkbox is checked, the frame panel color range is set automatically according to the selected auto range type: | |||
* '''Min-Max''' - the minimum and maximum value in the frame is set as ''Min Level'' and ''Max Level''. | |||
* '''0.XXX – 0XXX fractile''' – color range is set according to selected fractile. The fractile is approximately calculated from histogram of the frame with 1024 bins to reduce CPU time. What it means is, that a histogram of the frame values is made (1024 bins) and the values than according to fractile e.g. for 0.01-0.99 the<sub> </sub> 1% of lowest and highest values in histogram, are set as ''Min Level'' and ''Max Level''. | |||
Revision as of 14:59, 18 April 2023
Introduction
The PIXet Pro is a multi-platform software developed in ADVACAM company. It is a software package for Medipix family chips for acquisition control. It supports most of the available Medipix based devices (Medipix 2, Medipix3, Timepix, Medipix Quad, Timepix Quad, Widepix, Timepix3) and commonly used readout interfaces MiniPIX, FitPIX, ModuPIX, WidePIX, RasPIX, etc. Pixet provides many tools for optimization of detector parameters, data processing, image corrections and scripting. Pixet has an open architecture (not open source) supporting various types of imaging detectors and related devices (e.g. control of positioning systems or X-ray tubes) and allowing integration of user plug-in modules prepared in C++. Many of such plugins already exists, e.g. Timepix chip equalization, calibration, beam-hardening correction, flat-field correction, particle track analysis, scripting in Python with syntax highlighting. Pixet is written in C++ language and uses multi-platform Qt libraries.
Features
- Measures and reads data from Medipix detectors
- Visualizes the measured data
- Configures the detector
- Saves measured data in several formats (ASCII, PNG image, Pixel Log, …)
- Flat-field correction
- Calibration of measured data
- Beam hardening correction
- Cluster Analysis tool
- Multi-platform software (runs on Windows, Mac OS X, Linux)
System Requirements
Operating systems
- Windows 7
- Windows Server 2012
- Windows 8
- Windows 10
- Mac OS X 10.12 and higher
- Ubuntu Linux
- Debian Linux
- CentOS Linux
- RedHat Linux
Recommended system configuration
- Intel Pentium or equivalent processor with 1.5 GHz or faster
- 8 GB RAM
- Graphics mode 1280x800 with 16.7 m colors or higher
- 200 MB free hard disk space (additional space might be required for saving log files, configuration files and measured data)
- USB 2.0 port
Installation
Microsoft Windows
The PIXet for Windows is distributed as a single setup.exe file for automatic installation. For automatic installation just double-click the setup.exe and follow the instruction in the setup wizard.
In order to communicate with most of the devices, the PIXet needs the device drivers to be installed. In newer versions of Microsoft Windows, the drivers are installed automatically when the device is connected the first time. In a case that the drivers are not installed automatically, the drivers installation file Drivers/setup.exe is included in the distribution of the PIXet.
Mac OS X
The PIXet for Mac OS X system is distributed as a standard DMG file (disk image file). To install the Pixet, mount (double-click) the pixet.dmg file. A window with the disk content will open. To install, just move the Pixet folder to the Application folder.
There is no need to install a special driver for the devices. The software might ask first time it is launched after a reboot of the computer to unload Apple driver. The Apple driver is not compatible with our devices. Just click on the unload.
Linux
The Pixet for Linux system is distributed as a single tar file. To install, just untar the file. The software is launched by executing the pixet.sh script.
There is no need to install a special driver for the devices. In order to run the software under normal user, it is necessary adjust the permissions of our USB devices in udev system. This can be done by executing the script install_driver_rules.sh. It is also sometimes necessary to unload the system ftdi_sio driver. Just execute rmmod ftdi_sio as root in shell before running the software.
Main window of PIXet
Main window
The main window the software consists of device sidebar, frame (picture) panel where measured data are visualized, control panel on the right side, toolbar, menu bar, and status panel in the bottom. The panels on the right side can be minimized by clicking on the down arrow in the corresponding panel or can be hidden/shown via menu Panels.
Device sidebar
The device sidebar shows all the connected devices as icons. By clicking on each icon user can open frame panel and control panels of each device.
Frame Panel
The frame panel visualizes measured data (frames).
- Zooming area in the frame An area in the frame can be zoomed by holding the left mouse button in the frame, dragging the mouse to create a selection rectangle and releasing the mouse button. The area will be zoomed, scrollbars will appear and the X and Y axis will show exact location and size of the zoomed area. The zoomed area can be zoomed further by repeating the steps above.
- Moving zoomed area The zoomed area can be adjusted by using scrollbars or by dragging the picture with right mouse button.
Image Properties panel
This panel allows for adjusting of color range of the frame.
- Min level, Max level Adjusts the minimal and the maximal value of the frame that are visible in the frame panel. The values between Min level and Max level are then mapped to selected color map. In the case of the gray color map, minimal selected value is black and maximal value is white. To illustrate more clearly, let’s imagine we have a frame 3x3 with values as in the picture below and we set Min Level=1 and Max Level=5. The values under 1 (in this case 0) will not be visible and will be shown in lowest color (black). The values over selected range (in this case 6) will be show in the highest color (white). The rest of the values will be mapped to the 256 colors of the gray map, starting with dark colors for lower values and lighter colors for greater values.
| 5 | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | 4 | 1 |
| 5 | 6 | 2 |
- Auto range When the auto range checkbox is checked, the frame panel color range is set automatically according to the selected auto range type:
- Min-Max - the minimum and maximum value in the frame is set as Min Level and Max Level.
- 0.XXX – 0XXX fractile – color range is set according to selected fractile. The fractile is approximately calculated from histogram of the frame with 1024 bins to reduce CPU time. What it means is, that a histogram of the frame values is made (1024 bins) and the values than according to fractile e.g. for 0.01-0.99 the 1% of lowest and highest values in histogram, are set as Min Level and Max Level.