Binary core API: Difference between revisions
| (15 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
==== Where to get these files? ==== | ==== Where to get these files? ==== | ||
:All need files except XML configs are located in the zip file with name like us: ''' | : All need files except XML configs are located in the zip file with name like us: | ||
:'''Download:''' [https:// | ::'''API_PIXet_Pro_1.8.2_Windows_x86_64.zip''' | ||
::'''Download:''' [https://advacam.com/downloads/ Advacam download page]<br> | |||
: Be careful about the correct libraries, we supply | |||
:* Windows-x86-64b | |||
:* Linux-x86-64b | |||
:* Linux-ARM-32b | |||
:* Linux-ARM-64b | |||
<br> | |||
:And all files except LIB files for Windows compilation are located in the Pixet directory:<br> | :And all files except LIB files for Windows compilation are located in the Pixet directory:<br> | ||
[[File:Files-usable-for-SDK-in-Pixet.png|frame|none|alt=All files except LIB files for Windows compilation are located in the Pixet directory|All files except LIB files for Windows compilation are located in the Pixet directory]] | [[File:Files-usable-for-SDK-in-Pixet.png|frame|none|alt=All files except LIB files for Windows compilation are located in the Pixet directory|All files except LIB files for Windows compilation are located in the Pixet directory]] | ||
| Line 193: | Line 200: | ||
== C++ Windows CLR examples == | == C++ Windows CLR examples == | ||
=== AdvacamAPIexamples package === | === AdvacamAPIexamples package === | ||
This is the | This is the package of example apps for all device types. | ||
; Link | ; Link | ||
: https://advacam.com/examples/AdvacamAPIexamples.rar | : https://advacam.com/examples/AdvacamAPIexamples.rar | ||
: (MS Visual Studio 2017 Solution with C++ projects of Windows CLR programs) | : (MS Visual Studio 2017 Solution with C++ projects of Windows CLR programs) | ||
=== Examples using std future === | |||
This is the package of 2 small examples with '''paralell measuring''' at more devices, using '''std::future'''. Timepix3 only. | |||
: One is Windows '''CLR APP''', second is '''commandline''' | |||
; Link | |||
: https://advacam.com/examples/ExamplesUsingFuture.rar | |||
: (MS Visual Studio 2022 Solution with 2 C++ projects) | |||
== C# examples == | == C# examples == | ||
'''Notes:''' | '''Notes:''' | ||
* Use the release/64 bit configuration | * Use the release/64 bit configuration | ||
* Functions that have optional parameters in pxcapi.h (for example pxcInitialize) must be declared with all parameters and then called, for example, with zeros. | |||
* The working directory is directory with the exe file. Typically project\bin\Release. Copy pixet.ini and other auxilliary files here. | * The working directory is directory with the exe file. Typically project\bin\Release. Copy pixet.ini and other auxilliary files here. | ||
* In the MS Visual studio | * In the MS Visual studio 2022 (and may be other), project first not working. You must click Properties, change .NET version to old, save it, change .NET version back to actual and save. Now project can work. | ||
* Our API can also be used to produce cross-platform software. In that case, be careful about the correct libraries, we supply Windows-x86-64b / Linux-x86-64b / Linux-ARM-32b / Linux-ARM-64b. | |||
=== Simple C# commandline example === | === Simple C# commandline example === | ||
| Line 2,879: | Line 2,895: | ||
Specialy thick chips have a easily visible image distortion. Afther start-up, CdTe contains lot of free charges, they can cause problems duringearly measurements (use '''pxcDoSensorRefresh''').<br> | Specialy thick chips have a easily visible image distortion. Afther start-up, CdTe contains lot of free charges, they can cause problems duringearly measurements (use '''pxcDoSensorRefresh''').<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Si and CdTe have opposite bilas polarity | Si and CdTe have opposite bilas polarity. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 3,318: | Line 3,334: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
=Related= | = Related = | ||
*[[Pixet SDK]] | * [[Pixet SDK]] | ||
*[[Files and directories of the Pixet and SDK#Main directory of the API-using programs, independent on the Pixet|Files and directories: Main directory of the API-using programs]] | * [[Files and directories of the Pixet and SDK#Main directory of the API-using programs, independent on the Pixet|Files and directories: Main directory of the API-using programs]] | ||
* [[File types]] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:42, 11 December 2024
Core/basic binary (C/C++) API introduction
This API is part of the Advacam's Pixet SDK and allows access to functions of the Pixet Core.
The binary API parts are:
- Binary core/basic API (this document)
- Binary clustering API
- Binary spectral imaging API
See: Pixet SDK overview
Usage overview
- Settings of the device
- Getting information about the device
- Single-frame measurement
- Multi-frame measurement
- Continuous frame measurement (endless repeats and without dead time on some devices, Mpx3 and Tpx2 for example)
- Data-driven (pixel mode) measurement (Tpx3 only)
- Synchronized measurement
- TDI imaging - Scanning linearly moving objects, for example on a conveyor belt.
- Basic image bad pixel correction
- Beam hardening correction (Xray imaging has a very non-linear relationship between the thickness of the material and the intensity of the transmitted radiation. First, low-energy radiation is captured, followed by components that are significantly more penetrating.)
Libraries
The core API with the pxcore library, allowing basic measurements and device settings.
Files:
- pxcapi.h API header file
- pxcore.dll or pxcore.so binary libraries for Windows or Linux
- pxcore.lib static linging file for easier using on Windows (compile time only)
- common.h common file defining basic types, constatns and usefull macros. It's not necessary, but it can be useful.
And need some auxiliary files and directories:
Requirements
Hardware
This API requires computer with x86 compatible architecture or ARM with memory management features (no small MCU), 64bit Windows or Linux and connected some Advacam hardware with imaging chip. Medipix3, Timepix, Timepix2, Timepix3, etc. Some functions are universal for all hardwares (pxcInitialize, pxcGetDeviceName, etc), some is specialized for only one chip type (pxcMeasureSingleFrameTpx3 is Timepix3 only).
Specialized functions have names with chip type included:
- pxcSetTimepixCalibrationEnabled – Timepix only (no Timepix3)
- pxcMeasureTpx3DataDrivenMode – Timepix3 only
- pxcMeasureSingleFrameMpx3 – Medipix3 only
The attempt to use the function if compatible hardware (in initialized state) not present, end with error.
Return code is PXCERR_UNEXPECTED_ERROR.
Software
All the API functions have heads in pxcapi.h, implemented for Windows in the pxcore.dll and for linking must use the pxcore.lib in the linker settings. Implementation for Linux is in the libcore.so.
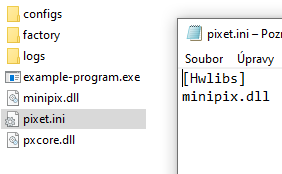
Compiled program need the pixet.ini file with proper hwlibs list inside, necessary hardware dll files (eq minipix.dll for Minipixes), optional special files (eq zestwpx.bit for Widepixes), subdirectory “factory” with default config files for all present imaging devices (eq MiniPIX-I08-W0060.xml) and the Pixet core will create subdirectory “configs” to save changed configs on exit.
See The Pixet core, additional libraries and other files
Usually, for build, just set the compiler to use 64bit and the linker to use the pxcore.lib file.
In Microsoft visual studio, while creating the C++ CLR project, it is also necessary to insert the use of WIN32 definition into the project settings (C/C++ / Preprocessor / Preprocessor definitions):
The Pixet core, additional libraries and other files
Main files:
- pxcapi.h API header file for importing to C/C++
- pxcore.dll or pxcore.so binary libraries for Windows or Linux
- pxcore.lib static linging file for easier using in C/C++ on Windows
And need some auxiliary files and directories:
Where to get these files?
- All need files except XML configs are located in the zip file with name like us:
- API_PIXet_Pro_1.8.2_Windows_x86_64.zip
- Download: Advacam download page
- Be careful about the correct libraries, we supply
- Windows-x86-64b
- Linux-x86-64b
- Linux-ARM-32b
- Linux-ARM-64b
- And all files except LIB files for Windows compilation are located in the Pixet directory:
Example of the project directory
On the right is a screenshot of the Windows CLR APP project directory in Visual Studio that uses Minipix Tpx3. The marked files were copied from the Advacam SDK and the "factory" directory contains the configuration
XML file for the device. It is important that the name is complete, eg MiniPIX-I08-W0060.xml. This file will be used on first launch.
The directory "configs" is created when Pixet core is terminated and contains a configuration XML file with saved current settings. This file will be used on each subsequent startup and updated on each subsequent exit.
The "logs" directory is created when Pixet core is started for the first time and contains LOG files from device activity and backups of these files for the last 10 starts.
Contents of the pixet.ini file:
[hwlibs] minipix.dll
(x64, Myform... and TPx3-1... are from the MS Visual studio project)
Don't forget to set up WIN32 and pxcore.lib in the project settings as described in the parent chapter.
Tip: How to create the Windows CLR APP:
MSDN:create-c-windows-forms-application-in-visual-studio-2017
Example of the minimalistic program directory
Some examples
Simple C commandline example and build
Example code
This is simple example of commandline C program, whitch initializes the Pixet core and device, sets it's operation mode, measures single frame, saves the frame to some files and deinitializes the Pixet core with all the connected devices.
(Timepix3 only)
#include "pxcapi.h"
int main() {
int rc; // return code
printf("Initializing...\n");
rc = pxcInitialize();
printf("pxcInitialize: %d (0 is OK)\n", rc);
rc = pxcSetTimepix3Mode(0, PXC_TPX3_OPM_TOATOT); // sets OPM of device with index 0
printf("pxcSetTimepix3Mode: %d (0 is OK)\n", rc);
// pxcMeasureMultipleFrames(deviceIndex, frameCount, acqTime, triggerSettings);
rc = pxcMeasureMultipleFrames(0, 3, 1, PXC_TRG_NO);
printf("pxcMeasureMultipleFrames: %d (0 is OK)\n", rc);
// pxcSaveMeasuredFrame(deviceIndex, frameLastIndex, filename);
rc = pxcSaveMeasuredFrame(0, 0, "testImg0.png");
printf("pxcSaveMeasuredFrame 0: %d (0 is OK)\n", rc);
rc = pxcSaveMeasuredFrame(0, 1, "testImg1.txt");
printf("pxcSaveMeasuredFrame 1: %d (0 is OK)\n", rc);
rc = pxcSaveMeasuredFrame(0, 2, "testImg2.pbf");
printf("pxcSaveMeasuredFrame 2: %d (0 is OK)\n", rc);
rc = pxcExit();
printf("pxcExit: %d (0 is OK)\n", rc);
}
Note: If You want test it in device other than Timepix3, You can comment lines with pxcSetTimepix3Mode. But then it is not clear what will be measured.
Building using cmake on Windows with Visual Studio installed
Example of CMakeLists.txt file for compiling this using cmake (C++ file is named "minipix1.cpp"):
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10)
project(minipix1)
# include_directories(${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR})
# link_directories(${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR})
add_library(pxcore SHARED IMPORTED)
set_property(TARGET pxcore PROPERTY IMPORTED_LOCATION "${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/pxcore.dll")
set_property(TARGET pxcore PROPERTY IMPORTED_IMPLIB "${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/pxcore.lib")
add_executable(minipix1 minipix1.cpp)
target_link_libraries(minipix1 pxcore)
Example of the Cmake building script:
rmdir /s /q build
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -DCMAKE_GENERATOR_PLATFORM=x64 ..
msbuild /P:Configuration=Release ALL_BUILD.vcxproj
cd ..
copy pxcore.dll build\Release\pxcore.dll
copy minipix.dll build\Release\minipix.dll
copy pixet.ini build\Release\pixet.ini
echo build\Release\minipix1.exe > run.cmd
User can finally run the run.cmd to run the program.
Building on Linux using GCC
Example build.sh:
#!/bin/bash
gcc -o build-out minipix1.cpp -Wno-write-strings -L. -lpxcore -ldl -lm -lc -g
Example run.sh to run the output executable:
#!/bin/bash
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=. ./build-out
# run last compiled example
- Troubleshooting
- Be careful of library, platform and system compatibility.
- That is, 32/64 bit, Intel vs ARM architecture and the use of unusual Linux distributions.
- Example error message: skipping incompatible ./libpxcore.so when searching for -lpxcore
- Be careful of gcc and it's libraries versions.
- If too old, some errors will occur.
- Example error message: undefined reference to symbol '_Znam@@GLIBCXX_3.4
C++ Windows CLR examples
AdvacamAPIexamples package
This is the package of example apps for all device types.
- Link
- https://advacam.com/examples/AdvacamAPIexamples.rar
- (MS Visual Studio 2017 Solution with C++ projects of Windows CLR programs)
Examples using std future
This is the package of 2 small examples with paralell measuring at more devices, using std::future. Timepix3 only.
- One is Windows CLR APP, second is commandline
- Link
- https://advacam.com/examples/ExamplesUsingFuture.rar
- (MS Visual Studio 2022 Solution with 2 C++ projects)
C# examples
Notes:
- Use the release/64 bit configuration
- Functions that have optional parameters in pxcapi.h (for example pxcInitialize) must be declared with all parameters and then called, for example, with zeros.
- The working directory is directory with the exe file. Typically project\bin\Release. Copy pixet.ini and other auxilliary files here.
- In the MS Visual studio 2022 (and may be other), project first not working. You must click Properties, change .NET version to old, save it, change .NET version back to actual and save. Now project can work.
- Our API can also be used to produce cross-platform software. In that case, be careful about the correct libraries, we supply Windows-x86-64b / Linux-x86-64b / Linux-ARM-32b / Linux-ARM-64b.
Simple C# commandline example
using System;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class Program {
[DllImport("pxcore.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern int pxcInitialize(Int32 a, UInt64 b);
[DllImport("pxcore.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern int pxcExit();
[DllImport("pxcore.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern int pxcGetDevicesCount();
static void Main(string[] args) {
int rc;
Console.WriteLine("pxcInitialize ...");
rc = pxcInitialize(0, 0);
Console.WriteLine($"rc={rc:D} (0 is OK)", rc);
Console.WriteLine("pxcGetDevicesCount...");
rc = pxcGetDevicesCount();
Console.WriteLine("rc={0:D}\n", rc);
if (rc > 0) {
// do something now
} else {
Console.WriteLine("No devices detected\n");
}
Console.WriteLine("pxcExit...");
rc = pxcExit();
Console.WriteLine("rc={0:D} (0 is OK)", rc);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Some more complex imports for inspiration:
[DllImport("pxcore.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern int pxcGetDeviceChipID(UInt32 deviceIndex, UInt32 chipIndex, StringBuilder chipIDBuffer, UInt32 size);
[DllImport("pxcore.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern int pxcGetDeviceDimensions(UInt32 deviceIndex, ref UInt32 width, ref UInt32 height);
[DllImport("pxcore.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern int pxcMeasureSingleFrameTpx3(UInt32 deviceIndex, double frameTime, [Out] double[] frameToaITot, [Out] UInt16[] frameTotEvent, ref UInt32 size, UInt32 trgStg = 0);
C# Windows desktop example
Xojo Basic Windows desktop example
See: Xojo windows example
API header definition
All API functions are defined in the pxcapi.h file. Each definition starting with the PXCAPI keyword:
#ifndef WIN32 // Linux
#define PXCAPI extern "C" __attribute__ ((visibility("default")))
#else // Windows
#define PXCAPI extern "C" __declspec(dllexport)
#endif
API auxiliary functions
This chapter describes auxiliary functions. There are need for normal using of the device, but it not measuring or processing data.
Start-up, end, errors
pxcInitialize
- This function initializes the Pixet software and all connected devices. This function has to be called first before any other function except pxcGetLastError. The init process of each device is:
- Initialize hardwrare and communication
- Try to load device XML config file from the "configs" dir
- If failed, try to load device XML config file from the "factory" dir
- Warning: If the correct config is not loaded, the device will not work properly and may do strange things.
See
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcInitialize(int argc = 0, char const* argv[] = NULL);
Parameters
- argc – number of program command line arguments (optional parameter)
- argv – command line program arguments (optional parameter)
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Can be imported with parameters int32,uint64 and called with 0,0. Usesfull in languages other than C/C++.
Example
int rc = pxcInitialize();
pxcExit
- This function deinitializes Pixet software and all the connected devices. This function has to be called as last function before unloading the pxcore library. The exit process of each device is:
- Save actual device XML config file to the "configs" dir
- Deinitialization of the hardware and communication
See
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcExit();
Parameters
- (no pars)
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
int rc = pxcExit();
pxcSetDirectories
- Sets the configuration files directory and directory for log files. Has to be set before calling the pxcInitialize function. Use it to change its default locations defined by pixet.ini.
See
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetDirectories(const char* configsDir, const char* logsDir);
Parameters
- configsDir – Path to the directory for loading/saving config files
- logsDir – Path to the directory for saving log files
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
pxcRefreshDevices
- This function looks for newly connected devices and removed disconnected devices from the device list.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcRefreshDevices();
Parameters
- (no pars)
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
int rc = pxcRefreshDevices();
pxcReconnectDevice
- If the device was disconnected or experienced communication problems, this function will try to reconnect the device and reinitialize it. Like as do the pxcExit and pxcInitialize, but only for one device index. The process is:
- Saves the device config to the “configs” directory
- Disconnects the device
- Connects the device
- Loads the device config
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcReconnectDevice(unsigned deviceIndex);
Parameters
- deviceIndex - index of the device, starting from zero
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
int rc = pxcReconnectDevice(0); // reconnect device with index 0
pxcGetLastError
- Returns text of last error. This function can be called even before pxcInitialize()
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetLastError(char* errorMsgBuffer, unsigned size);
Parameters
- errorMsgBuffer - buffer where text will be saved
- size - size of supplied buffer
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
char msg[200];
pxcGetLastError(msg, 200);<br> printf("Error msg: %s\n", msg);
Example1 (console)
#define ERRMSG_BUFF_SIZE 512
#define ENTER_ON true
#define ENTER_OFF false
// (the function used in most examples in this manual)
void printErrors(const char* fName, int rc, bool enter) {
char errorMsg[ERRMSG_BUFF_SIZE];
pxcGetLastError(errorMsg, ERRMSG_BUFF_SIZE);
if (errorMsg[0]>0) {
printf("%s %d err: %s", fName, rc, errorMsg);
} else {
printf("%s %d err: ---", fName, rc);
}
if (enter) printf("\n");
}
Now you can use it:
rc = pxcSetTimepix3Mode(deviceIndex, PXC_TPX3_OPM_EVENT_ITOT);
printErrors("pxcSetTimepix3Mode", rc, ENTER_ON);
If mode set was suscessfull, result is:
- pxcSetTimepix3Mode 0 err: ---
If not, you can see some as:
- pxcSetTimepix3Mode -2 err: Invalid device index
Example2 (Windows CLR)
const unsigned cErrBufSize = 512;
// primary use to show function name, return code, last error message
bool errorToList(const char* fName, int rc) {
char errorMsg[cErrBufSize];
char cMsg[cErrBufSize];
String^ eMsg;
pxcGetLastError(errorMsg, cErrBufSize);
if (rc!=0) {
sprintf(cMsg, "%s %d err: %s", fName, rc, errorMsg);
eMsg = gcnew String(errorMsg);
} else {
sprintf(cMsg, "%s %d err: ---", fName, rc);
};
String^ sMsg = gcnew String(cMsg);
listMessages->Items->Add(sMsg);
return (rc!=0);
}
Now you can use it:
rc = pxcSetTimepix3Mode(deviceIndex, PXC_TPX3_OPM_EVENT_ITOT);
if (errorToList("pxcSetTimepix3Mode", rc)) return rc;
pxcGetIPixet
- Returns a core pointer for processing libraries, Clustering or Spectral imaging for example.
- Definition
PXCAPI void* pxcGetIPixet((void));
Parameters
- (no pars)
- Return value
- core pointer
Parameter Get/Set functions (direct)
Functions described in this chapter working directly, function name defines parameter name and type.
For named parameters settings see: Parameter Get/Set functions (using text paramName)
Example: Setting operation mode
// Set the operating mode
rc = pxcSetTimepix3Mode(deviceIndex, PXC_TPX3_OPM_TOATOT);
printErrors("pxcSetTimepix3Mode", rc);
Example: List of devices with parameters
#include <stdio.h>
#include "pxcapi.h"
#define CHT_Si 0
#define CHT_CdTe 1
char chipType = CHT_Unknown;
int main(int argc, char const* argv[]) { // #######################################
int rc = pxcInitialize();
if (rc) {
printf("Could not initialize Pixet:\n");
printErrors("pxcInitialize", rc, ENTER_ON);
return -1;
}
int connectedDevicesCount = pxcGetDevicesCount();
printf("Connected devices: %d\n", connectedDevicesCount);
if (connectedDevicesCount == 0) return pxcExit();
for (unsigned devIdx = 0; (signed)devIdx < connectedDevicesCount; devIdx++) {
char deviceName[256];
memset(deviceName, 0, 256);
pxcGetDeviceName(devIdx, deviceName, 256);
char chipID[256];
memset(chipID, 0, 256);
pxcGetDeviceChipID(devIdx, 0, chipID, 256);
printf("Device %d: Name %s, (first ChipID: %s)\n", devIdx, deviceName, chipID);
}
double bias;
rc = pxcGetBias(devIdx, &bias);
if (bias < 0.0) {
if (devIdx == 0) chipType = CHT_CdTe;
printf("Chip material detected: CdTe\n");
} else if (bias == 0.0) {
printf("Chip material not detected!\n");
} else {
if (devIdx == 0) chipType = CHT_Si;
printf("Chip material detected: Si\n");
}
printf("=================================================================\n");
// here can be working code (calling some example function from this manual)
return pxcExit();
}
pxcGetDevicesCount
- This function returns number of connected and initialized devices.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetDevicesCount();
Parameters
- (no pars)
- Return value
- Number of devices, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code
Example
printf("Connected devices count: %d\n", pxcGetDevicesCount());
pxcListNetworkDevices
- Searches for available network devices and store basic information about it to arrary. This is special function, independent of the Pixet Core. Can be used for listing devices without the PXcore initialized to prevent "steal" of other devices on the network. The output is usesfull to browse/testing network devices, it's IPs and availability on the network subnets.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcListNetworkDevices(NetworkDevInfo* devInfos, unsigned* size);
Parameters
- devInfos - Pointer to array of NetworkDevInfo{char ip[15]; char name[20]; int serial;} structures
- size - [in] Pointer to size of the devInfo (number of elements) / [out] Value overwritten by the number of devices found
- Return value
- Returns 0 if OK or PXCERR_BUFFER_SMALL if the number of devices exceeded the size of the array (the array is still filled and *size is set)
Note
- 1. Can be used independent of the Pixet core.
2. A related feature is planned, allowing you to select devices to be used by PXcore. Currently you can write to the zest.ini instead.
Example
NetworkDevInfo ndi[256];
unsigned ndiSize = 256;
int rc;
msgToList("pxcListNetworkDevices...");
//pxcListNetworkDevices(NetworkDevInfo* devInfos, unsigned* size);
rc = pxcListNetworkDevices(ndi, &ndiSize);
errorToList("pxcListNetworkDevices", rc);
if (rc != 0 && rc != PXCERR_BUFFER_SMALL) return;
for (int n=0; n < ndiSize; n++) {
msgToList(String::Format(" IP: {0}\t Name: {1}\t SN: {2}", gcnew String(ndi[n].ip), gcnew String(ndi[n].name), ndi[n].serial));
}
if (ndiSize == 0) msgToList(" (no devs found)");
else if (rc == PXCERR_BUFFER_SMALL) msgToList(" (and more devs than ndi array size)");
Network device info details:
struct NetworkDevInfo{
char ip[15];
char name[20];
int serial;
};
pxcGetDeviceInfo
- Gets device info structure and returns devType. If *devInfo is NULL, only returns devType.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetDeviceInfo(unsigned deviceIndex, CDevInfo *devInfo);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- devInfo – pointer to CDevInfo struct
- Return value
- Device type number
Example
// simple use:
if (pxcGetDeviceInfo(devIdx, NULL) != TPX3) errorMsg("The device is not Timepix3");
// Advanced use:
CDevInfo devInfo[20];
char *dtStrings[] = {"Tpx", "Mpx3", "Tpx3", "Tpx2"};
for (int n=0; n<pxcGetDevicesCount(); n++) {
pxcGetDeviceInfo(n, devInfo[n]);
printf("DevIdx %d: Name: %s, SN: %d, DevType: %s", n, devInfo[n].name, devInfo[n].serial, dtStrings[devInfo[n].type+1]);
}
Device info details:
enum DevType{
TPX = 1, MPX3, TPX3, TPX2,
};
struct CDevInfo{
char name[20];
int serial;
DevType type;
};
pxcGetDeviceName
- This function returns the full name of the selected device.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetDeviceName(unsigned deviceIndex, char* nameBuffer, unsigned size);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- nameBuffer – buffer where the name of the device will be saved. Cannot be NULL
- size – size of the supplied name buffer
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
char name[100];
pxcGetDeviceName(deviceIndex, name, 100);
printf("Dev %d name: %s\n", deviceIndex, name);
pxcGetDeviceChipCount
- This function returns number of chips in the device.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetDeviceChipCount(unsigned deviceIndex);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- Return value
- Number of chips if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
printf("Dev %d has chip count: %d\n", deviceIndex, pxcGetDeviceChipCount(deviceIndex));
pxcGetDeviceChipID
- This function returns the ID of chip of the detector connected to the readout device.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetDeviceChipID(unsigned deviceIndex, unsigned chipIndex, char* chipIDBuffer, unsigned size);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- chipIndex – index of the chip in the device, starting from zero
- chipIDBuffer – buffer where the chipID of the detector will be saved. Cannot be NULL
- size - size of the supplied chipID buffer
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
char id[50];
int rc = pxcGetDeviceChipID(deviceIndex, 0, id, 50);
if (rc==0) printf("Chip 0 of dev %d have ID: %s\n", deviceIndex, id);
else printf("pxcGetDeviceChipID failed, code: %d\n", rc);
pxcGetDeviceSerial
- This function returns the devise serial number.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetDeviceSerial(unsigned deviceIndex);
Parameters
- deviceIndex - index of the device, starting from zero
- Return value
- Serial number (>0) if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
printf("Dev %d has serial number: %d\n", deviceIndex, pxcGetDeviceSerial(deviceIndex));
pxcGetDeviceDimmensions
- This function gets pixel width and height of the device.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetDeviceDimmensions(unsigned deviceIndex, unsigned *w, unsigned *h);
Parameters
- deviceIndex - index of the device, starting from zero
- w – pointer to unsigned variable where the width of the device will be returned
- h – pointer to unsigned variable where the height of the device will be returned
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
unsigned w, h;
int rc = pxcGetDeviceDimmensions(deviceIndex, &w, &h);
if (rc==0) printf("Width: %d, Height %d [px]\n", w, h);
else printf("pxcGetDeviceDimmensions failed, code %d\n", rc);
pxcGetBias
- This function gets the bias voltage (high voltage) of the sensor chip.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetBias(unsigned deviceIndex, double* bias);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- bias – pointer to double variable where current bias will be returned
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
double bias;
int rc = pxcGetBias(deviceIndex, &bias);
if (rc==0) printf("Bias: %f V\n", bias);
else printf("pxcGetBias failed, code %d\n", rc);
pxcGetBiasRange
- This function gets the range of the allowed minimal and maximal bias values.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetBiasRange(unsigned deviceIndex, double* minBias, double* maxBias);
Parameters
- deviceIndex - index of the device, starting from zero
- minBias – pointer to double variable where minimum allowed bias will be returned
- maxBias – pointer to double variable where maximum allowed bias will be returned
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
double min, max;
int rc = pxcGetBiasRange(deviceIndex, &min, &max);
if (rc==0) printf("Bias min: %f, max: %f V\n", min, max);
else printf("pxcGetBiasRange failed, code %d\n", rc);
pxcSetBias
- This function sets the high voltage (bias) of the detector.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetBias(unsigned deviceIndex, double bias);
Parameters
- deviceIndex - index of the device, starting from zero
- bias – high voltage in volts (limits and polarity depending on the device configuration, see: pxcGetBiasRange)
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
int rc = pxcSetBias(0, -350); // set bias -350 V to device with idx 0
pxcGetThreshold
- This function gets the threshold of the detector. Output value is normally in keV, but if the device not properly configurated, output is didital DAC value.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetThreshold(unsigned deviceIndex, unsigned thresholdIndex, double* threshold);
Parameters
- deviceIndex - index of the device, starting from zero
- thresholdIndex – for all except Medipix3 always 0, for Medipix3 index of corresponding threshold starting from zero
- threshold – pointer to double variable where threshold will be saved. The value is several keVs with decimals or from 0 to a some power of two (depending of device DAC bits depth).
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
double thl;
int rc = pxcGetThreshold(deviceIndex, &thl);
if (rc==0) printf("Threshold: %f\n", thl);
else printf("pxcGetThreshold failed, code %d\n", rc);
pxcGetThresholdRange
- This function gets the allowed range of values for threshold. Output values are normally in keV, but if the device not properly configurated, output is didital DAC value.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetThresholdRange(unsigned deviceIndex, int thresholdIndex, double* minThreshold, double* maxThreshold);
Parameters
- deviceIndex - index of the device, starting from zero
- thresholdIndex – for Timepix and Timepix3 always 0, for Medipix3 index of corresponding threshold starting from zero
- minThreshold – pointer to double variable where the minimal allowed threshold will be returned
- maxThreshold – pointer to double variable where the maximal allowed threshold will be returned
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
double min, max;
int rc = pxcGetThresholdRange(deviceIndex, &min, &max);
if (rc==0) printf("Threshold range - min: %f, max: %f\n", min, max);
else printf("pxcGetThresholdRange failed, code %d\n", rc);
pxcSetThreshold
- This function sets the threshold of the detector in KeV.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetThreshold(unsigned deviceIndex, unsigned thresholdIndex, double threshold);
Parameters
- deviceIndex - index of the device, starting from zero
- thresholdIndex - for Timepix and Timepix3 always 0, for Medipix3 index of corresponding threshold starting from zero
- threshold – detector threshold in keV.
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Warning
- Too low thl value cause many noising pixels with all related problems.
Example
int rc = pxcSetThreshold(1, 0, 4.5); // set threshold with idx 0 on device with idx 1 to the 4.5 keV.
pxcGetDAC
- This function gets a single DAC value of the detector.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetDAC(unsigned deviceIndex, unsigned chipIndex, unsigned dacIndex, unsigned short* value);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- chipIndex – index of the chip, starting from zero
- dacIndex – index of the DAC, starting from zero
- value – pointer to output value be stored
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
unsigned short val;
int rc = pxcGetDAC(deviceIndex, chipIndex, dacIndex, &val);
if (rc==0) printf("Input value of DAC with idx %d, on chip with idx %d, of device with idx %d is: %d\n", deviceIndex, chipIndex, dacIndex, val);
else printf("pxcGetDAC failed, code %d\n", rc);
pxcSetDAC
- This function sets a single DAC value of the detector.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetDAC(unsigned deviceIndex, unsigned chipIndex, unsigned dacIndex, unsigned short value);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- chipIndex – index of the chip, starting from zero
- dacIndex – index of the DAC, starting from zero
- value – new DAC value
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
int rc = pxcSetDAC(0, 1, 2, 123); // set DAC with idx 3 on chip with idx 2 on device with idx 1 to the 123.
pxcGetTimepixClock
- This function gets the current value of measurement clock for Timepix detector (in MHz).
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetTimepixClock(unsigned deviceIndex, double* clock);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- clock – pointer to double variable where the clock will be saved
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Timepix devices, not usable on Timepix3 and other TimepixN. Timepix3 has a fixed clock of 40 MHz. Timepix2 has other clocks managenment.
Example
double val;
int rc = pxcGetTimepixClock(deviceIndex, &val);
if (rc==0) printf("Timepix clock: %f MHz\n", val);
else printf("pxcGetTimepixClock failed, code %d\n", rc);
pxcSetTimepixClock
- This function sets the value of measurement clock for Timepix detector (in MHz). Not all values are possible, the result will be the closest possible frequency.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetTimepixClock(unsigned deviceIndex, double clock);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- clock – desired value of the measurement clock for Timepix detector
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Timepix devices, not usable on Timepix3 and other TimepixN. Timepix3 has a fixed clock of 40 MHz. Timepix2 has other clocks managenment.
Example
int rc = pxcSetTimepixClock(deviceIndex, 25.0);
pxcGetTimepixMode
- This function gets the current value of the Timepix mode (Counting, Energy,…)
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetTimepixMode(unsigned deviceIndex);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- Return value
- Timepix mode if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
- Timepix mode can be:
- PXC_TPX_MODE_MEDIPIX – counting mode
- PXC_TPX_MODE_TOT – energy mode
- PXC_TPX_MODE_TIMEPIX – timepix mode if successful.
- Otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Timepix devices, not usable on Timepix3 and other TimepixN.
Example
int rc = pxcGetTimepixMode(deviceIndex);
if (rc>=0) printf("Mode of dev. idx %d is: %d\n", deviceIndex, rc);
else printf("pxcGetTimepixMode failed, code %d\n", rc);
pxcSetTimepixMode
- This function sets the value of Timepix mode.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetTimepixMode(unsigned deviceIndex, int mode);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- mode – new value of the Timepix mode. One of the values:
- PXC_TPX_MODE_MEDIPIX – counting mode
- PXC_TPX_MODE_TOT – energy mode
- PXC_TPX_MODE_TIMEPIX – timepix mode
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Timepix devices, not usable on Timepix3 and other TimepixN.
Example
int rc = pxcSetTimepixMode(0, PXC_TPX_MODE_MEDIPIX); // set dev 0 to mode counting alias MEDIPIX
pxcSetTimepixCalibrationEnabled
- This function enables or disables the calibration of Timepix ToT counts to energy in keV
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetTimepixCalibrationEnabled(unsigned deviceIndex, bool enabled);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- enabled – if the calibration is enabled or disable
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Timepix devices, not usable on Timepix3 and other TimepixN.
Example
int rc = pxcSetTimepixCalibrationEnabled(0, true); // enable ToT calibration to keVs on device with idx 0
pxcIsTimepixCalibrationEnabled
- This function returns if the calibration of Timepix ToT counts to energy in keV is enabled.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcIsTimepixCalibrationEnabled(unsigned deviceIndex);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- Return value
- 0 if disabled, greater than 0 enabled, negative value a PXCERR_XXX code
Note
- Only for the Timepix devices, not usable on Timepix3 and other TimepixN.
Example
int rc = pxcIsTimepixCalibrationEnabled(0);
if (rc>=0) printf("Calibration of dev0 is %s\n", (rc==0) ? "disabled" : "enabled");
else printf("pxcIsTimepixCalibrationEnabled failed, code %d\n", rc);
pxcGetTimepix2Clock
- This function gets the current clocks settings in the Timepix2 detector.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetTimepix2Clock(unsigned deviceIndex, double* totClock, double* toaClock, unsigned* divider);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- totClock – pointer to double variable where the ToT clock (in MHz) will be saved
- toaClock – pointer to double variable where the ToA clock (in MHz) will be saved
- divider – pointer to unsigned int variable where the divider value will be saved
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Timepix2 devices, not usable on Timepix3 and other Timepix. Timepix3 have a fixed
clock of 40 MHz.
pxcSetTimepix2Clock
- This function sets Timepix2 detector clocks settings.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetTimepix2Clock(unsigned deviceIndex, double clock, unsigned divider);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- clock – desired new value of the ToT clock (in MHz) for the Timepix2 detector. The real frequency will be nearest possible division by 2’s power from the 50 MHz. Min is 1.5625 MHz.
- divider – value of the ToA divider index.
- Values means 0: disable, 1: no division, 2-30: div. by 2n-1.
- The ToA clock will be divided from the ToT clock.
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Timepix2 devices, not usable on Timepix3 and other Timepix. Timepix3 have a fixed clock of 40 MHz.
Warning
- The factory energy calibration is only for the 50 MHz ToA clock.
pxcSetTimepix2Mode
- This function sets the value of Timepix2 mode
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetTimepix2Mode(unsigned deviceIndex, int mode);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- mode – new value of the Timepix2 mode. One of the values:
- PXC_TPX2_OPM_TOT10_TOA18
- PXC_TPX2_OPM_TOT14_TOA14
- PXC_TPX2_OPM_CONT_TOT10_CNT4
- PXC_TPX2_OPM_CONT_TOT14
- PXC_TPX2_OPM_CONT_TOA10
- PXC_TPX2_OPM_CONT_TOA14
- PXC_TPX2_OPM_CONT_CNT10
- PXC_TPX2_OPM_CONT_CNT14
- PXC_TPX2_OPM_ITOT10_TOA18
- PXC_TPX2_OPM_ITOT14_TOA14
- PXC_TPX2_OPM_CONT_ITOT10_CNT4
- PXC_TPX2_OPM_CONT_ITOT14
- Modes desctiption
- TOT – time of threshold in ToT ticks, or energy if calibrated
- TOA – time of arrival in ToA ticks
- CNT – count of hits
- ITOT – integrated time of threshold in the pixel, or estimate energy if calibrated
- CONT – continual mode: One counter set counting while reading data from other counter set
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Timepix2 devices, not usable on Timepix3 and other Timepix.
pxcSetTimepix2AdaptiveGainMode
- This function sets the value of Timepix2 mode.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetTimepix2AdaptiveGainMode(unsigned deviceIndex, bool adaptiveGainOn);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- adaptiveGainOn – enable the adaptive gain feature
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Timepix2 devices, not usable on Timepix3 and other Timepix.
pxcSetTimepix2AnalogueMaskingMode
- This function sets the value of Timepix2 mode
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetTimepix2AnalogueMaskingMode(unsigned deviceIndex, bool analogMaskOn);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- analogMaskOn – enable the analogue masking feature
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Timepix2 devices, not usable on Timepix3 and other Timepix.
pxcSetTimepix2CalibrationEnabled
- This function enables or disables the calibration of Timepix ToT counts to energy in keV
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetTimepix2CalibrationEnabled(unsigned deviceIndex, bool enabled);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- enabled – if the calibration is enabled or disable
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Different acquisition or frame reading functions needed if calibration is on or off.
- Only for the Timepix2 devices, not usable on Timepix3 and other Timepix.
pxcIsTimepix2CalibrationEnabled
- This function returns if the calibration of Timepix ToT counts to energy in keV is enabled
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcIsTimepix2CalibrationEnabled(unsigned deviceIndex);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Different acquisition or frame reading functions needed if calibration is on or off.
- Only for the Timepix2 devices, not usable on Timepix3 and other Timepix.
pxcSetTimepix3Mode
- Sets the operation mode of Timepix3 detector
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetTimepix3Mode(unsigned deviceIndex, int mode);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- mode – mode of the detector PXC_TPX3_OPM_XXX values
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Timepix3 devices, not usable on other Timepixes or Medipixes.
pxcSetTimepix3CalibrationEnabled
- Enables/disables the calibration of Timepix3 ToT counts to energy in keV. If enabled, output of a frame maesurements on the device will be calibrated.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetTimepix3CalibrationEnabled(unsigned deviceIndex, bool enabled);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- enabled – if calibraiton is enabled
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Calibration working properly only if the device has loaded proper config.
pxcIsTimepix3CalibrationEnabled
- Gets if the calibration of Timepix3 ToT counts to energy in keV is enabled. See pxcSetTimepix3CalibrationEnabled for details.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcIsTimepix3CalibrationEnabled(unsigned deviceIndex);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- Return value
- enabled > 0, disabled = 0, error < 0 – the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
pxcSetMedipix3OperationMode
- Sets the operation mode of Medipix3 detector
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetMedipix3OperationMode(unsigned deviceIndex, int opMode);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- opMode – mode of the detector PXC_MPX3_OPM_XXX values
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Medipix3 devices, not usable on Timepixes or other Medipixes.
pxcSetMedipix3GainMode
- Sets the gain mode of Medipix3 detector
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetMedipix3GainMode(unsigned deviceIndex, int gain);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- gain – mode of the detector PXC_MPX3_GAIN_MOD_XXX values
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Medipix3 devices, not usable on Timepixes or other Medipixes.
pxcSetMedipix3AcqParams
- Sets acquisition parameters for Medipix3
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetMedipix3AcqParams(unsigned deviceIndex, bool colorMode, bool csm, int gain, bool equalize);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- colorMode – if color mode is enabled
- csm – if charge sharing mode is enabled
- gain – gain settings (PXC_MPX3_GAIN_XXX values)
- equalize – if equalization bit in Medipix3 is enabled
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Medipix3 devices, not usable on Timepixes or other Medipixes.
pxcSetMedipix3MatrixParams
- Sets parameters of the Meidpix3 pixel matrix
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetMedipix3MatrixParams(unsigned deviceIndex, int depth, int counter, int colBlock, int rowBlock);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- depth – depth of the counters PXC_MPX3_CNTD_XXX values
- counter – selected counter (PXC_MPX3_CNT_XXX values)
- colBlock – region of interest readout (PXC_MPX3_COLB_XXX values)
- rowBlock – region of interest readout (PXC_MPX3_ROWB_XXX values)
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Medipix3 devices, not usable on Timepix or other Medipixes.
pxcSetPixelMatrix
- Sets the pixel matrix configuration. This is low level function for advanced users.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetPixelMatrix(unsigned deviceIndex, unsigned char* maskMatrix, unsigned size);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- maskMatrix – pixel mask matrix. 0 masked, 1 unmasked
- size – size of the mask matrix
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
pxcGetPixelMatrix
- Gets the pixel matrix configuration. This is low level function for advanced users.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetPixelMatrix(unsigned deviceIndex, unsigned char* maskMatrix, unsigned byteSize);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- maskMatrix – buffer where the mask matrix will be stored. 0 masked, 1 unmasked
- size – size of the mask matrix
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Metadata
Various devices, readout chips, detector chips and measurement methods have various metadata. To obtain informations about all relevant metadata for your purphose, set-up and run the testmeasurement with file-saving (using test code or Pixet program). Now you can read the accompanying DSC/INFO files, that contains all metadata for this combination of device/detector/measurement.
- Example DSC records
- "Chips layout" ("Order of chips in matrix"):
- i32[5]
- 4 3 0 1 2
- "Start time" ("Acquisition start time"):
- double[1]
- 1659611081.595321
- "Start time (string)" ("Acquisition start time (string)"):
- char[64]
- Thu Aug 4 13:04:41.595321 2022
pxcGetMetaDataValue
- This function gets measured data meta data value. Output value is converted to char*.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetMetaDataValue(unsigned deviceIndex, unsigned dataIndex, const char* metaDataName, char* valueBuffer, unsigned* size);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- dataIndex - index of the measured data (frame), starting from zero
- metaDataName – name of the metadata to get, "Start time" for example
- valueBuffer – buffer where the value of the meta data as string will be stored
- size – pointer to size of the supplied buffer
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
char mdb[200]; // metadata buffer
unsigned mdbs = 200; // metadata buffer size
char mdn[] = "Start time"; // metadata name
int rc = pxcGetMetaDataValue(deviceIndex, frameLastIndex, mdn, mdb, &mdbs);
if (rc != 0) errorToList("pxcGetMetaDataValue", rc);
else msgToList("Acquisition start time: " + gcnew String(mdb));
Parameter Get/Set functions (using text paramName)
In this chapter are a functions that working with named parameters. Alias readout parameters: Because originally it was only about the parameters of the readout chips. Later, the setting of other device and software parameters was also added.
For dirrect setting functions see: Parameter Get/Set functions (direct)
Example:
// Data Driven Block Size [B], default 66000
rc = pxcSetDeviceParameter(deviceIndex, "DDBlockSize", 6000);
printf("pxcSetDeviceParameter %d", rc);
Warning: Most parameters are for testing purposes only and you will not need them in normal use.
pxcGetDeviceParameter
- Returns the value of integer device parameter (e.g. settings of trigger)
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetDeviceParameter(unsigned deviceIndex, const char* parameterName);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- parameterName – name of the device parameter
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
pxcSetDeviceParameter
- Sets a value of the integer device parameter (e.g. settings of trigger)
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetDeviceParameter(unsigned deviceIndex, const char* parameterName, int parameterValue);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- parameterName – name of the device parameter
- parameterValue – new value of the parameter
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
pxcGetDeviceParameterDouble
- Returns the value of device double parameter
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetDeviceParameterDouble(unsigned deviceIndex, const char* parameterName, double* parameterValue);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- parameterName – name of the device parameter
- parameterValue – pointer to double variable where the parameter value will be saved
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
pxcSetDeviceParameterDouble
- Sets a value of the device double parameter
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetDeviceParameterDouble(unsigned deviceIndex, const char* parameterName, double parameterValue);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- parameterName – name of the device parameter
- parameterValue – new value of the parameter
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
pxcGetDeviceParameterString
- Returns the value of device string parameter
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetDeviceParameterString(unsigned deviceIndex, const char* parameterName, const char* parameterValue, unsigned size);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- parameterName – name of the device parameter
- parameterValue – pointer to string buffer where the parameter value will be saved
- size – size of the passed buffer
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
pxcSetDeviceParameterString
- Sets a value of the device string parameter
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetDeviceParameterString(unsigned deviceIndex, const char* parameterName, const char* parameterValue);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- parameterName – name of the device parameter
- parameterValue – new value of the parameter
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Tpx3 parameter names list
Warning: Most parameters are for testing purposes only and you will not need them in normal use.
#define PAR_LIBVER "HwLibVer"
#define PAR_DEBUGLOG "DebugLog"
#define PAR_DUMMYACQ "DummyAcqNegativePolarity"
#define PAR_TEMP "Temperature"
#define PAR_TEMP_CHIP "TemperatureChip"
#define PAR_TEMP_CPU "TemperatureCpu" // mimipix/tpx3 only
#define PAR_TEMP_CHIP_CPU "TemperatureChipCpu" // mimipix/tpx3 only
#define PAR_TEMP_READ_ACQSERIE "TemperatureReadBeforeAcqSerie" // mimipix/tpx3 only
#define PAR_TEMP_READ_EVERYACQ "TemperatureReadBeforeEachAcq" // mimipix/tpx3 only
#define PAR_TEMP_CHECK_IN_SW "CheckMaxTempInSW" // mimipix/tpx3 only
#define PAR_TEMP_CHECK_IN_CPU "CheckMaxChipTempInCPU" // mimipix/tpx3 only
#define PAR_TEMP_MAX_ALLOWED_TEMP "MaxAllowedChipTemp" // mimipix/tpx3 only
#define PAR_DAC_BANGAP "DacBandGap"
#define PAR_DAC_TEMP "DacTemp"
#define PAR_BIAS_SENSE_VOLT "BiasSenseVoltage"
#define PAR_BIAS_SENSE_CURR "BiasSenseCurrent"
#define PAR_DD_BUFF_SIZE "DDBuffSize"
#define PAR_DD_BLOCK_SIZE "DDBlockSize"
#define META_SHUTTER_TIME "Shutter open time" // mimipix/tpx3 only
#define PAR_CHAN_MASK "ChanMask" // no net/tpx3
#define PAR_READOUT_CLOCK "ReadoutClock" // no net/tpx3
#define PAR_TRG_STG "TrgStg"
#define PAR_TRG_TIMESTAMP "TrgTimestamp"
#define PAR_TRG_T0SYNC_RESET "TrgT0SyncReset"
#define PAR_TRG_READY "TrgReady" // no net/tpx3
#define PAR_TRG_OUTLEVEL "TrgOutLevel" // mimipix/tpx3 only
#define PAR_TRG_OUT_ENABLE "TrgOutEnable" // mimipix/tpx3 only
#define PAR_TRG_IS_MASTER "IsMaster"
#define PAR_MOTOHOURS "Motohours" // mimipix/tpx3 only
#define PAR_MTX "MTX" // mimipix/tpx3 only
#define PAR_SEND_TOA_PIXELS "SendDummyToaPixels" // mimipix/tpx3 only
#define PAR_DUMMYSPEED "DDDummyDataSpeed" // no mimipix/tpx3
#define PAR_BLOCKCOUNT "BlockCount" // no mimipix/tpx3
#define PAR_PROCESSDATA "ProcessData" // no mimipix/tpx3
#define PAR_TRG_MULTI "TrgMulti" // no mimipix/tpx3
#define PAR_ADVAPIX_ADC "AdvaPixADC" // no mimipix/tpx3
#define PAR_TRG_READY "TrgReady" // zem only
#define PAR_TRG_CMOS "TrgCmos" // zem only
#define PAR_READOUT_CLOCK "ReadoutClock" // zem only
Tpx2 parameter names list
Warning: Most parameters are for testing purposes only and you will not need them in normal use.
const static char* PAR_LIBVER = "HwLibVer";
const static char* PAR_DEBUGLOG = "DebugLog";
const static char* PAR_BIAS_SENSE_VOLT = "BiasSenseVoltage";
const static char* PAR_BIAS_SENSE_CURR = "BiasSenseCurrent";
const static char* PAR_READOUT_CLOCK = "ReadoutClock";
const static char* PAR_TRG_STG = "TrgStg";
const static char* PAR_TRG_IS_MASTER = "IsMaster";
const static char* PAR_MOTOHOURS = "Motohours";
const static char* PAR_TEMP_CPU = "TemperatureCpu";
const static char* PAR_TEMP_MAX_ALLOWED_TEMP = "MaxAllowedChipTemp";
const static char* PAR_POWER_VOLT = "PowerSupplyVoltage";
const static char* PAR_CPU_SUPPLY_VOLT = "CPUSupplyVoltage";
const static char* PAR_CHIP_LDO_VOLT = "ChipLDOVoltage";
const static char* PAR_INPUT_CURRENT = "DeviceInputCurrent";
const static char* PAR_CHIP_CURRENT = "ChipCurrent";
Mpx2 (Timepix) parameter names list
Warning: Most parameters are for testing purposes only and you will not need them in normal use.
#define PAR_LIBVER "HwLibVer" // all, include minipixes
#define PAR_DEBUGLOG "DebugLog" // all, include minipixes
#define CFG_BINPIXCFG "BinaryPixelCfg" // fei-minipix only
#define PAR_FIRMWARE "Firmware" //widepix only
#define PAR_PS_COUNT "PreShutterClockCount"
#define PAR_PS_DIVIDER "PreShutterClockDivider"
#define PAR_PS_DELAY "PreShutterDelayClockCount"
#define PAR_TEMP "Temperature" // no zem
#define PAR_BIASINCPU "BiasInCpu" // widepix only
#define PAR_TRG_STG "TriggerStg"
#define PAR_TRG_WAITREADY "TriggerWaitForReady"
#define PAR_TRG_MASTER "TriggerMaster"
#define PAR_TRG_OUTLEVEL "TriggerOutLevel"
#define PAR_TRG_ALTERNATIVE "TriggerAlternative" // fitpix only
#define PAR_TRG_TWODEVS "TriggerTwoDevs" // fitpix only
#define PAR_BURST_DISABLE "BurstDisable" // fitpix only
#define PAR_CPU_BIAS_SET "*BiasSet" // widepix only
#define PAR_CPU_BIAS_VOLTSENSE "BiasVolt" // widepix only
#define PAR_CPU_BIAS_CURRSENSE "BiasCurr" // widepix only
#define PAR_CPU_TEMP_DET "TempDet" // widepix only
#define PAR_FASTACQ "FastAcq" // zem only
#define PAR_BURST_FRAME_COUNT "BurstFrameCount" // zem only
#define PAR_PIXEL_BUFFSIZE "PixelBuffSize" // zem only
Mpx3 parameter names list
Warning: Most parameters are for testing purposes only and you will not need them in normal use.
#define PAR_LIBVER "HwLibVer"
#define PAR_DEBUGLOG "DebugLog"
#define PAR_TEMP "Temperature"
#define PAR_TRG_STG "TriggerStg"
#define PAR_TRG_WAITREADY "TriggerWaitForReady"
#define PAR_TRG_MASTER "TriggerMaster"
#define PAR_TRG_OUTLEVEL "TriggerOutLevel"
#define PAR_TRG_SERIES "TriggerTdiSeries"
#define PAR_TDI_ROWCOUNT "TdiRowCount"
#define PAR_BIASINCPU "BiasInCpu"
#define PAR_BIAS_DISCHARGE "BiasDischarge"
#define PAR_CPU_BIAS_SET "*BiasSet"
#define PAR_CPU_BIAS_VOLTSENSE "BiasVolt"
#define PAR_CPU_BIAS_CURRSENSE "BiasCurr"
#define PAR_CPU_TEMP_DET "TempDet"
Zest-wpxdev parameter names list
Warning: Most parameters are for testing purposes only and you will not need them in normal use.
const static char* PAR_LIBVER = "HwLibVer";
const static char* PAR_FIRMWARE = "Firmware";
const static char* PAR_FIRMWARE_CPU = "FirmwareCpu";
const static char* PAR_DEBUGLOG = "DebugLog";
const static char* PAR_TEMP = "Temperature";
const static char* PAR_TRG_STG = "TriggerStg";
const static char* PAR_TRG_WAITREADY= "TriggerWaitForReady";
const static char* PAR_TRG_MASTER = "TriggerMaster";
const static char* PAR_TRG_OUTLEVEL = "TriggerOutLevel";
const static char* PAR_BIAS_DISCHARGE = "BiasDischarge";
Zem-wpx7dev parameter names list
Warning: Most parameters are for testing purposes only and you will not need them in normal use.
#define PAR_LIBVER "HwLibVer"
#define PAR_DEBUGLOG "DebugLog"
#define PAR_PS_COUNT "PreShutterClockCount"
#define PAR_PS_DIVIDER "PreShutterClockDivider"
#define PAR_PS_DELAY "PreShutterDelayClockCount"
#define PAR_ENC_PULSE_CNT "EncoderPulseCount"
#define PAR_ENC_PULSE_DIR "EncoderDirection"
#define PAR_ENC_PULSE_COUNTER "EncoderPulseCounter"
Other auxilliary functions
pxcLoadDeviceConfiguration
- This function loads device configuration from xml file
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcLoadDeviceConfiguration(unsigned deviceIndex, const char* filePath);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- filePath – path to xml configuration file
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
pxcSaveDeviceConfiguration
- This function saves device configuration to xml file
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSaveDeviceConfiguration(unsigned deviceIndex, const char* filePath);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- filePath – path to xml configuration file
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
pxcSetupTestPulseMeasurement
- Enables / Disables and setups parameters of the test pulse measurements
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetupTestPulseMeasurement(unsigned deviceIndex, bool tpEnabled, double height, double period, unsigned count, unsigned spacing);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- tpEnabled – enables/disables test pulse measurement (in functions Measure..Frame(s))
- height – test pulse height (0 – 1.5 V)
- period – single test pulse period (1 – 256 us)
- count – number of test pulses (1 – 10000)
- spacing – spacing that is used during measurement (sub acquisition), good value is 4
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
pxcRegisterAcqEvent
- Registers an acquisition event callback that is called when corresponding event occurs
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcRegisterAcqEvent(unsigned deviceIndex, const char* event, AcqEventFunc func, intptr_t userData);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- event – event name (PXC_ACQEVENT_XXX values)
- func – callback function of type AcqEventFunc
- userData – user data that are passed to callback function. Use this as pointer or as 32/64bit integer, depending on system pointer size. The callback function will receive the userData value.
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
The AcqEventFunc definition:
typedef void (*AcqEventFunc)(intptr_t eventData, intptr_t userData);
pxcUnregisterAcqEvent
- Unregisters the acquisition event callback
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcUnregisterAcqEvent(unsigned deviceIndex, const char* event, AcqFunc func, intptr_t userData);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- event – event name (PXC_ACQEVENT_XXX values)
- func – callback function of type AcqFunc
- userData – user data pointer that was used in pxcRegisterAcqEvent, for proper indetify the event
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
pxcSetSensorRefresh
- Sets the sensor refresh sequence text. The sensor refresh is used to clean the sensor of free charges. Process containing sequence of bias changes. Suitable values depend on chip manufacturing technology details.
- For more details see: pxcDoSensorRefresh
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSetSensorRefresh(unsigned deviceIndex);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- refreshString – sensor refresh string
- refresh string defines steps with pairs of times [sec] and bias coefficients [1=100%]
- (physical bias values limited to min/max chip properties, see pxcGetBiasRange)
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Warning
- Special function for scientific or device developing using. Normally it not usesfull, normally use the default refresh parameters loaded from factory config.
Example
// (devIdx, "time1, coef1; time2, coef2; time3, coef3; ...")
int rc = pxcSetSensorRefresh(0, "5, 2; 3, 1.5; 1, 1.2; 1, 1");
printErrors("pxcSetSensorRefresh", rc, ENTER_ON);
pxcDoSensorRefresh
- Performs the sensor refresh. The sensor refresh is used to clean the sensor of free charges. Process containing sequence of bias changes and may take several seconds.
- Useful for devices with CdTe or CZT chip:
- Before the measurement, which should start right after the initialization.
- To improve the repeatability of measurements
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcDoSensorRefresh(unsigned deviceIndex);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- This is an analog part refresh, not a recovery from a digital failure.
pxcEnableSensorRefresh
- Enables automatic sensor refresh before each acquisition series and at periodic intervals.
- For more details see: pxcDoSensorRefresh
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcEnableSensorRefresh(unsigned deviceIndex, bool enabled, double refreshTime);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- enabled – if automatic sensor refresh is enabled
- refreshTime – sensor refresh is performed repeatedly after this time in seconds.
- If thime is 0, then the refresh is done only once before the measurement
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- This is an analog part refresh, not a recovery from a digital failure.
pxcEnableTDI
- Enables TDI (Time Delayed Integration) measurement (if device supports it, single line Mpx3 for example). Usesful for scanning of linearly moving objects.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcEnableTDI(unsigned deviceIndex, bool enabled);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- enabled – if TDI is enabled
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
pxcIsReadyForSoftwareTrigger
- Checks if the device is ready to accept software trigger.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcIsReadyForSoftwareTrigger(unsigned deviceIndex);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- Return value
- 1 if ready, 0 if not ready, and negative if error, PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- If you want to use this immediately after a function for starting acquisition, wait until it's ready by using pxcIsReadyForSoftwareTrigger.
Example
int rc = pxcIsReadyForSoftwareTrigger(deviceIndex);
if (rc==1) msgToList("Dev is ready to SW trigger");
else if (rc==0) msgToList("Dev is not ready to SW trigger");
else errorToList("pxcIsReadyForSoftwareTrigger", rc);
pxcDoSoftwareTrigger
- Sends the software trigger: Start of acquisition with trgStg=PXC_TRG_SWSTART used.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcDoSoftwareTrigger(unsigned deviceIndex);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
API frame-based measuring functions
The functions described in this chapter are used for frame-based measurements. Suitable for imaging, for example. After acquisition ends, you can read all the frame data (65536 pixels from every chip) to your buffer or save to the file. Acquisition can start by software (afther call a function, for example), or by HW trigger. Data types depends on chip technology and the operation mode.
Chip can generate one or two data blocks (event count and integrated times over threshold, for example) in one acquisition. Do not forget to set the operation mode. If mode not set, some devices measure something, but some other devices measure something else in this case.
- Example projects
- MiniPixTpx3-Frames – mode set, single frame, multiple frames with/without callback, continuous measuring
pxcMeasureSingleFrame
- Performs a measurement of single frame and returns its data
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcMeasureSingleFrame(unsigned deviceIndex, double frameTime, unsigned short* frameData, unsigned* size, unsigned trgstg);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- frameTime – time of the measurment in seconds
- frameData – pointer to buffer where data will be saved. For single detector size is 65536
- size – pointer to varible with the size of the buffer. The actual size will be output to this variable
- trgStg – settings of external trigger - one of the PXC_TRG_XXX values. Default PXC_TRG_NO.
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- This function have only one framebuffer. This is fully sufficient for single-output devices and modes. In combined modes (ToA+ToT, Event+IToT, dual threshold) only first data are available (ToA, Event, Threshold0). To take both outputs from the combined modes, it is necessary to use specialized functions for the given type of detector.
pxcMeasureSingleFrameMpx3
- Performs a measurement of single frame and returns its data. This is only for Medipix3 chips
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcMeasureSingleFrameMpx3(unsigned deviceIndex, double frameTime, unsigned* frameData1, unsigned* frameData2, unsigned* size, unsigned trgstg);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- frameTime – time of the measurment in seconds
- frameData1 – pointer to buffer where data from first counter will be saved. For single detector chip, size is 65536
- frameData2 – pointer to buffer where data from second counter will be saved. For single detector chip, size is 65536
- size – pointer to varible with the size of the buffer. The actual size will be output to this variable
- trgStg – settings of external trigger - one of the PXC_TRG_XXX values. Default PXC_TRG_NO.
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Medipix3 devices, not usable on Timepix or other Medipixes.
pxcMeasureSingleFrameTpx3
- Performs a measurement of single frame and returns its data. This is only for Timepix3 detector.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcMeasureSingleFrameTpx3(unsigned deviceIndex, double frameTime, double* frameToaITot, unsigned short* frameTotEvent, unsigned* size, unsigned trgstg);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- frameTime – time of the measurment in seconds
- frameToaITot – pointer to buffer where data from ToA or iToT counter (based on set operation mode) will be saved. For single detector chip, size is 65536
- frameTotEvent – pointer to buffer where data from ToT or Event counter (based on set operation mode) will be saved. For single detector chip, size is 65536
- size – pointer to varible with the size of the buffer. The actual size will be output to this variable
- trgStg – settings of external trigger - one of the PXC_TRG_XXX values. Default PXC_TRG_NO.
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Timepix3 devices, not usable on other Timepixes or Medipixes.
Example
void pxcMeasureSingleFrameTpx3Test(unsigned di) { // di – device index ========
int rc; // return codes
const unsigned cSize = 65536; // chip pixels count
unsigned short frameTotEvent[cSize]; // frame data - event count
double frameToaITot[cSize]; // frame data - integrated time over threshold
double time = 1.0; // frame acquisition time
unsigned size = cSize; // buffer size and measured data size
int mode = PXC_TPX3_OPM_EVENT_ITOT;
rc = pxcSetTimepix3Mode(di, mode);
printErrors("pxcSetTimepix3Mode", rc, ENTER_ON);
rc = pxcMeasureSingleFrameTpx3(di, time, frameToaITot, frameTotEvent, &size, PXC_TRG_NO);
printErrors("pxcMeasureSingleFrameTpx3", rc, ENTER_ON);
showFrameDual(frameTotEvent, frameToaITot, mode);
}
pxcMeasureSingleFrameTpx2
- Performs a measurement of single frame and returns its data. This is only for Timepix2 detector and only if calibration is disabled
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcMeasureSingleFrameTpx2(unsigned deviceIndex, double frameTime, unsigned* frameData1, unsigned* frameData2, unsigned* size, unsigned trgStg);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- frameTime – time of the measurment in seconds
- frameData1 – pointer to buffer where data from the first counter (based on set operation mode) will be saved. For single detector chip, size is 65536
- frameData2 – pointer to buffer where data from the second counter (based on set operation mode) will be saved. For single detector chip, size is 65536
- size – pointer to varible with the size of the buffer. The actual size will be output to this variable
- trgStg – settings of external trigger - one of the PXC_TRG_XXX values. Default PXC_TRG_NO.
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Timepix2 devices, not usable on other Timepixes or Medipixes.
- Only if Timepix2 calibration is disabled.
Example
void pxcMeasureSingleFrameTpx2Test(unsigned di) { // di – device index ========
int rc; // return codes
const unsigned cSize = 65536; // chip pixels count
unsigned frameData1[cSize]; // frame data - ToT data
unsigned frameData2[cSize]; // frame data - ToA data
double time = 1.0; // frame acquisition time
unsigned size = cSize; // buffer size and measured data size
int mode = PXC_TPX2_OPM_TOT10_TOA18;
rc = pxcSetTimepix2Mode(di, mode);
printErrors("pxcSetTimepix2Mode", rc, ENTER_ON);
rc = pxcMeasureSingleFrameTpx2(di, time, frameData1, frameData2, &size, PXC_TRG_NO);
printErrors("pxcMeasureSingleFrameTpx2", rc, ENTER_ON);
showFrameDual(frameData1, frameData2, mode);
}
pxcMeasureSingleCalibratedFrameTpx2
- Performs a measurement of single frame, calibrate ToT to energy and returns data. This is only for Timepix2 detector and only if calibration is enabled
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcMeasureSingleCalibratedFrameTpx2(unsigned deviceIndex, double frameTime, double* frameData1, unsigned* frameData2, unsigned* size, unsigned trgStg);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- frameTime – time of the measurment in seconds
- frameData1 – pointer to buffer where data from the first counter (based on set operation mode) will be saved. For single detector chip, size is 65536
- frameData2 – pointer to buffer where data from the second counter (based on set operation mode) will be saved. For single detector chip, size is 65536
- size – pointer to varible with the size of the buffer. The actual size will be output to this variable
- trgStg – settings of external trigger - one of the PXC_TRG_XXX values. Default PXC_TRG_NO.
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Timepix2 devices, not usable on other Timepixes or Medipixes.
- Only if Timepix2 calibration is enabled.
Example
void pxcMeasureSingleCalibratedFrameTpx2Test(unsigned di) { // di – device index =====
int rc; // return codes
const unsigned cSize = 65536; // chip pixels count
double frameData1[cSize]; // frame data - ToT data = calibrated to energy
unsigned frameData2[cSize]; // frame data - ToA data
double time = 1.0; // frame acquisition time
unsigned size = cSize; // buffer size and measured data size
int mode = PXC_TPX2_OPM_TOT10_TOA18;
rc = pxcSetTimepix2Mode(di, mode);
printErrors("pxcSetTimepix2Mode", rc, ENTER_ON);
rc = pxcMeasureSingleCalibratedFrameTpx2(di, time, frameData1, frameData2, &size, PXC_TRG_NO);
printErrors("pxcMeasureSingleCalibratedFrameTpx2", rc, ENTER_ON);
showFrameDual(frameData1, frameData2, mode);
}
pxcMeasureMultipleFrames
- Performs a measurement of several frames to memory
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcMeasureMultipleFrames(unsigned deviceIndex, unsigned fameCount, double frameTime, unsigned trgStg);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- frameCount – numeber of frames to measure
- frameTime – time of the measurment in seconds
- trgStg – settings of external trigger - one of the PXC_TRG_XXX values. Default PXC_TRG_NO
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
void pxcMeasureMultipleFramesTpx3Test() { // =========================
int rc; // return codes
const unsigned cSize = 65536; // chip pixels count
unsigned short frameTotEvent[cSize]; // frame data - event count
double frameToaITot[cSize]; // frame data - integrated time over threshold
double frameTime = 1.0; // frame acquisition time
unsigned frameCount = 5; // frame count
unsigned size = cSize; // buffer size and measured data size
int mode = PXC_TPX3_OPM_EVENT_ITOT;
rc = pxcSetTimepix3Mode(0, mode);
printErrors("pxcSetTimepix3Mode", rc, ENTER_ON);
printf("measuring %d frames...\n", frameCount);
pxcMeasureMultipleFrames(0, frameCount, frameTime, PXC_TRG_NO);
printErrors("pxcMeasureMultipleFrames", rc, ENTER_ON);
for (unsigned n=0; n<frameCount; n++) {
rc = pxcGetMeasuredFrameTpx3(0, n, frameToaITot, frameTotEvent, &size);
printErrors("pxcGetMeasuredFrameTpx3", rc, ENTER_ON);
size = cSize;
showFrameDual(frameTotEvent, frameToaITot, mode);
}
}
pxcMeasureMultipleFramesWithCallback
- Performs a measurement of several frames to memory. When each frame is measured, the supplied callback function is called and the userData parameter is passed as argument.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcMeasureMultipleFramesWithCallback(unsigned deviceIndex, unsigned fameCount, double frameTime, unsigned trgStg, FrameMeasuredCallback callback, intptr_t userData);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- frameCount – numeber of frames to measure
- frameTime – time of the measurment in seconds
- trgStg – settings of external trigger - one of the PXC_TRG_XXX values. Default PXC_TRG_NO.
- callback – pointer to function of FrameMeasuredCallback type
- userData – pointer to some user object/memory that is passed in callback function
- See pxcRegisterAcqEvent for userData details
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
void pxcMeasureMultipleFramesWithCallbackTestTpx3(unsigned deviceIndex) { // ==============
int rc; // return codes
double frameTime = 1;
unsigned frameCount = 5;
tMmfClbData usrData;
usrData.di = deviceIndex;
usrData.opm = PXC_TPX3_OPM_EVENT_ITOT;
rc = pxcSetTimepix3Mode(deviceIndex, usrData.opm);
printErrors("pxcSetTimepix3Mode", rc, ENTER_ON);
rc = pxcMeasureMultipleFramesWithCallback
(deviceIndex, frameCount, frameTime, PXC_TRG_NO, mmfCallback, (intptr_t)&usrData);
printErrors("pxcMeasureMultipleFramesWithCallback", rc, ENTER_ON);
// Measure function ends, after all callbacks are serviced
}
void mmfCallback(intptr_t acqCount, intptr_t userData) { // =================================
int rc; // return codes
const unsigned cSize = 65536; // chip pixels count
unsigned short frameTotEvent[cSize]; // frame data - event count
double frameToaITot[cSize]; // frame data - integrated time over threshold
unsigned size = cSize; // buffer size and measured data size
tMmfClbData usrData = *((tMmfClbData*)userData); // data transferred from start function
printf("mmfCallback acqCount=%d, di=%d\n", (unsigned)acqCount, usrData.di);
rc = pxcGetMeasuredFrameTpx3
(usrData.di, (unsigned)acqCount - 1, frameToaITot, frameTotEvent, &size);
printErrors("pxcGetMeasuredFrameTpx3", rc, ENTER_OFF); printf(", size=%d\n", size);
if (rc == 0) {
printf("Measured frame index %lu, ", (unsigned)acqCount - 1);
printf("count %d\n", pxcGetMeasuredFrameCount(usrData.di));
showFrameDual(frameTotEvent, frameToaITot, usrData.opm);
}
}
//The acqCount contains count of measured frames that are currently waiting in memory.
// You can use acqCount-1 as frame index to read.
// The userData is 64b number used to transfer some data from starting function to callback function.
// You can use it as data pointer like in this example, or simply as number with some overtyping.
typedef struct { // structure for userData, that is using in mmfCallback
unsigned di; // device index
int opm; // operation mode
} tMmfClbData;
pxcMeasureContinuous
- Performs an “endless” measurement of several frames to memory. The measurement is run until it’s aborted by pxcAbortMeasurement function. When each frame is measured, the supplied callback function is called and the userData parameter is passed as argument.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcMeasureContinuous(unsigned deviceIndex, unsigned fameBufferSize, double frameTime, unsigned trgStg, FrameMeasuredCallback callback, intptr_t userData);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- frameBufferSize – number of frames in circular buffer
- frameTime – time of the measurment in seconds
- trgStg – settings of external trigger - one of the PXC_TRG_XXX values. Default PXC_TRG_NO.
- callback – pointer to function of FrameMeasuredCallback type
- userData – pointer to some user object/memory that is passed in callback function
- See pxcRegisterAcqEvent for userData details
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- This function, differently to other multi-frame measurements, not waiting for process end. It simply start measurement and program continue next.
- You can set-up the callback by 2 ways:
- Simply use pointer to callback function in the pxcMeasureContinuous function. After do it, the commandline program must not leave the function in which pxcMeasureContinuous was used until the measurement is canceled.
- First use the pxcRegisterAcqEvent to set-up the callback, second use pxcMeasureContinuous without callback pointer or with NULL. Now it is possible to leave the superior function and measuring continue working independent. Afther cancel of the measurement, may be needed use the pxcUnregisterAcqEvent before other use of the Acq event.
Warning
- Aborting measuremet from its callback (like as in commandline example bellow) can cause lags for tens of seconds. If the pxcAbortMeasurement called by other way (Button event in GUI for example), abort is fast.
Example
void pxcMeasureContinuousTestTpx3(unsigned deviceIndex) { // ==============================
int rc; // return codes
double frameTime = 2;
unsigned buffrerFrames = 3;
tMmfClbData usrData;
usrData.di = deviceIndex;
usrData.cnt = 0; // num of frames to stop in callback (0 endless)
usrData.opm = PXC_TPX3_OPM_EVENT_ITOT;
rc = pxcSetTimepix3Mode(deviceIndex, usrData.opm);
printErrors("pxcSetTimepix3Mode", rc, ENTER_ON);
// method 1 (single step):
//rc = pxcMeasureContinuous (deviceIndex, buffrerFrames, frameTime, PXC_TRG_NO, mcCallback, (intptr_t)&usrData);
//printErrors("pxcMeasureContinuous", rc, ENTER_ON);
// method 2 (2 steps):
// register event
pxcRegisterAcqEvent(0, PXC_ACQEVENT_ACQ_FINISHED, mcCallback, (intptr_t)&usrData);
printErrors("pxcRegisterAcqEvent", rc, ENTER_ON);
// start continuous measuring (method 2, step 2)
rc = pxcMeasureContinuous(deviceIndex, buffrerFrames, frameTime);
printErrors("pxcMeasureContinuous", rc, ENTER_ON);
printf("waiting for callbacks...\n");
getchar(); // waiting so that callbacks can come
printf("pxcMeasureContinuousTest: user end\n");
}
/*The callback function is some as used in pxcMeasureMultipleFramesWithCallback example, but usrData structure contains
extra member, the cnt.This can be used to stop, whitch is additional in the callback: */
static unsigned cnt = 0;
cnt++;
if (usrData.cnt > 0 && cnt >= usrData.cnt) {
// stop continuous measuring on user defined number of frames
printf("pxcAbortMeasurement...");
rc = pxcAbortMeasurement(usrData.di);
printErrors("pxcAbortMeasurement", rc, ENTER_ON);
printf("Press enter to exit the program.\n");
}
pxcAbortMeasurement
- Stopts the currently running measurement on the indexed device.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcAbortMeasurement(unsigned deviceIndex);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Warning
- Aborting measuremet from its callback (like as in commandline example in pxcMeasureContinuous) can cause lags for tens of seconds. If the pxcAbortMeasurement called by other way (Button event in GUI for example), abort is fast.
pxcGetMeasuredFrameCount
- Returns number of measured frames in memory. Usesful with pxcMeasureMultipleFrames.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetMeasuredFrameCount(unsigned deviceIndex);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
pxcSaveMeasuredFrame
- Saves the measured frame to a file on the harddrive. This can be used instead of the pxcGetMeasuredFrame.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcSaveMeasuredFrame(unsigned deviceIndex, unsigned frameIndex, const char* filePath);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- frameIndex – index of the frame, starting from zero
- filePath – path to the file where frame will be saved
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
void someCallback(intptr_t acqCount, intptr_t userData) { // ======================
int rc; // return codes
tMmfClbData usrData = *((tMmfClbData*)userData);
rc = pxcSaveMeasuredFrame(usrData.di, (unsigned)acqCount - 1, "testFile.txt");
printErrors("pxcSaveMeasuredFrame-txt", rc, ENTER_ON);
rc = pxcSaveMeasuredFrame(usrData.di, (unsigned)acqCount - 1, "testFile.png");
printErrors("pxcSaveMeasuredFrame-txt", rc, ENTER_ON);
/* List of file extensions (format automatically detected by extension in filename):
#define PX_EXT_ASCII_FRAME "txt"
#define PX_EXT_BINARY_FRAME "pbf"
#define PX_EXT_MULTI_FRAME "pmf"
#define PX_EXT_BINARY_MULTI_FRAME "bmf"
#define PX_EXT_COMP_TPXSTREAM "pcts"
#define PX_EXT_TPX3_PIXELS "t3p"
#define PX_EXT_TPX3_PIXELS_ASCII "t3pa"
#define PX_EXT_TPX3_RAW_DATA "t3r"
#define PX_EXT_FRAME_DESC "dsc"
#define PX_EXT_INDEX "idx"
#define PX_EXT_CLUSTER_LOG "clog"
#define PX_EXT_PIXEL_LOG "plog"
#define PX_EXT_PNG "png"
#define PX_EXT_PIXET_RAW_DATA "prd"
(t3.. formats not frames - cannot be used with pxcSaveMeasuredFrame) */
}
pxcGetMeasuredFrame
- Gets data of specified measured frame from memory
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetMeasuredFrame(unsigned deviceIndex, unsigned fameIndex, unsigned short* frameData, unsigned* size);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- frameIndex – index of the frame, starting from zero
- frameData – pointer to buffer where data will be saved. For single chip detector size is 65536.
- size – pointer to varible with the size of the buffer. The actual size will be output to this variable.
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- This function have only one framebuffer. This is fully sufficient for single-output devices and modes. In combined modes (ToA+ToT, Event+IToT, dual threshold) only first data are available (ToA, Event, Threshold0). To take both outputs from the combined modes, it is necessary to use specialized functions for the given type of detector.
pxcGetMeasuredFrameTpx2
- Gets data of specified measured frame from memory.
- For Timepix2 chip only and only if calibration disabled.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetMeasuredFrameTpx2(unsigned deviceIndex, unsigned frameIndex, unsigned* frameData1, unsigned* frameData2, unsigned* size);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- frameIndex – index of the frame, starting from zero
- frameData1 – pointer to buffer where data from the first counter (based on set operationmode) will be saved. For single detector chip size is 65536
- frameData2 – pointer to buffer where data from the second counter (based on set operation mode) will be saved. For single chip detector size is 65536
- size - pointer to varible with the size of the buffer. The actual size will be output to this variable
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Timepix2 devices, not usable on other Timepixes or Medipixes.
- For Timepix2 chip only and only if calibration disabled.
pxcGetMeasuredCalibratedFrameTpx2
- Gets data of specified measured frame with calibration from memory.
- For Timepix2 chip only and only if calibration enabled.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetMeasuredCalibratedFrameTpx2(unsigned deviceIndex, unsigned frameIndex, double* frameData1, unsigned* frameData2, unsigned* size);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- frameIndex – index of the frame, starting from zero
- frameData1 – pointer to buffer where calibrated ToT->Energy data from the first counter (based on set operationmode) will be saved. For single detector chip size is 65536
- frameData2 – pointer to buffer where data from the second counter (based on set operation mode) will be saved. For single chip detector size is 65536
- size - pointer to varible with the size of the buffer. The actual size will be output to this variable
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Timepix2 devices, not usable on other Timepixes or Medipixes.
- For Timepix2 chip only and only if calibration enabled.
pxcGetMeasuredFrameTpx3
- Gets data of specified measured frame from memory. For Timepix3 chip only.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetMeasuredFrameTpx3(unsigned deviceIndex, unsigned fameIndex, double* frameToaITot, unsigned short* frameToTEvent, unsigned* size);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- frameIndex – index of the frame, starting from zero
- frameToaITot – pointer to buffer where data from ToA or iToT counter (based on set operation mode) will be saved. For single chip detector, size is 65536
- frameTotEvent – pointer to buffer where data from ToT or Event counter (based on set operation mode) will be saved. For single chip detector, size is 65536
- size – pointer to varible with the size of the buffer. The actual size will be output to this variable
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Only for the Timepix3 devices, not usable on other Timepixes or Medipixes.
API data-driven measuring functions
The functions described in this chapter can be used if frame-based measurement is not good choice, in particle collision research, for example.
Data-driven "frameless" in comparsion with frames:
- Advantages
- It is possible to continual measure for any length of time and repeated pixel hits are not lost.
- Disadvantages
- Each pixel is transmitted as a separate packet, including its position. Therefore, this mode is significantly more demanding on the transmission speed.
Afther measurement start, data from every event is stored in the buffer. Pixels has structures (defined in the pxcapi.h):
typedef struct _Tpx3Pixel {
double toa; // time of arrival [1 ns]
float tot; // time over threshold [25 ns] or energy [keV] if calibrated
unsigned int index; // index of pixel position
} Tpx3Pixel;
#pragma pack(push, 1)
typedef struct _RawTpx3Pixel {
u32 index: 24;
u64 toa: 64;
byte overflow: 1;
byte ftoa: 5;
u16 tot: 10;
} RawTpx3Pixel;
#pragma pack(pop)
See: The RawTpx3Pixel structure in memory
The Pixet core has a circular buffer in memory. The default size is 100 MB. There are blocks in the buffer. The default block size is 66000 bytes. Incoming data is stored in a block. The “new data” event (that can start the callback or save the blockt to file) occurs if:
- The data size reaches the block size
- Some data is in block over the timeout (500 ms)
- The measurement ends
If you need to process data more often, you can set smaller block size. But if blocks are too small, data transfer speed can fall and some data can be lost. This can occurs if block size is less than approximately 5000 bytes (depends on computer speed and other circumstances).
- Example projects
- MiniPixTpx3-DataDriven, commandline example – Set the parameters, use the callback and display the data, some auxiliary things and data convert. Save data to files. Without threads.
- AdvacamAPIexamples/Tpx3, Windows GUI CLR app – All common functions including data-driven measurements. Using threads.
- Note
- Functions in this chapter is only for the Timepix3 devices, not usable on other Timepixes or Medipixes.
pxcMeasureTpx3DataDrivenMode
- Performs a measurement with Timepix3 detector in Data Driven Mode (event by event mode, when stream of pixels is sent). Timepix3 only.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcMeasureTpx3DataDrivenMode(unsigned deviceIndex, double measTime, const char* filename, unsigned trgStg, AcqEventFunc callback, intptr_t userData);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- measTime – the total time of the measurement in seconds. Use 0 for infinite.
- filename – output file name and path (extensions must end *.t3pa, *.trp, *.t3r)
- trgStg – settings of external trigger - one of the PXC_TRG_XXX values. Default PXC_TRG_NO
- callback – pointer to function of acqEventFunc type
- userData – pointer to some user object/memory that is passed in callback function
- See pxcRegisterAcqEvent for userData details
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
int rc = pxcMeasureTpx3DataDrivenMode(0, 15, "testfile.t3pa");
// Measure for 15 seconds on device 0 with saving to the "testfile.t3pa" file
- Example for online processing
void timepix3DataDrivenGetPixelsTest(unsigned deviceIndex) { // ============================
int rc; // return codes
double measTime = 30;
int devIdx = deviceIndex; // transmitted over pointer for use in the callback function
// working with TOA, TOATOT, TOT_NOTOA, not working with EVENT_ITOT
rc = pxcSetTimepix3Mode(deviceIndex, PXC_TPX3_OPM_TOA);
printErrors("pxcSetTimepix3Mode", rc, ENTER_ON);
rc = pxcSetDeviceParameter(deviceIndex, PAR_DD_BLOCK_SIZE, 6000); // block [B]
printErrors("pxcSetDeviceParameter", rc, ENTER_OFF);
rc = pxcSetDeviceParameter(deviceIndex, PAR_DD_BUFF_SIZE, 100); // buffer [MB]
printf(", %d", rc);
rc = pxcSetDeviceParameter(deviceIndex, PAR_DCC_LEVEL, 80);
printErrors(",", rc, ENTER_ON); // data consistency check level (50-150) (*)
rc = pxcMeasureTpx3DataDrivenMode(deviceIndex, measTime, "", PXC_TRG_NO, onTpx3Data, (intptr_t)&devIdx);
printErrors("pxcMeasureTpx3DataDrivenMode", rc, ENTER_ON);
}
// * Data consistency check level : Detection level of ToA data inconsistency.
// If the chip is overloaded due too many partickes in time, clock can freezeand a ToA inconsistency occurrs.
// If it is detedted, measuring immediately stopand error “Acquisition failed(Data flow corrupted !!)“ occurrs.
// Level 50 is some like OFF, level 150 is highest sensitivity.
void onTpx3Data(intptr_t eventData, intptr_t userData) { // ================================
int deviceIndex = *((unsigned*)userData);
unsigned pixelCount = 0;
int rc; // return codes
rc = pxcGetMeasuredTpx3PixelsCount(deviceIndex, &pixelCount);
printErrors("getMeasuredTpx3PixelsCount", rc, ENTER_OFF);
printf(" PixelCount: %u\n", pixelCount);
auto result = new Tpx3Pixel[pixelCount];
rc = pxcGetMeasuredTpx3Pixels(deviceIndex, result, pixelCount);
printErrors("pxcGetMeasuredTpx3Pixels", rc, ENTER_ON);
dataUsingFunction(&result, pixelCount);
delete[] result;
}
pxcGetMeasuredTpx3PixelsCount
- Gets the number of measured Timepix3 pixels in data driven mode. Timepix3 only.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetMeasuredTpx3PixelsCount(unsigned deviceIndex, unsigned* pixelCount);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- pixelCount – pointer to output variable for number of pixels
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Example
unsigned int cnt;
int rc = pxcGetMeasuredTpx3PixelsCount(0, &cnt);
if (rc==0) printf("%d pixels from device idx 0 are waiting in memory\n", cnt);
else printf("pxcGetMeasuredTpx3PixelsCount failed, code %d\n", rc);
pxcGetMeasuredTpx3Pixels
- Gets the measured Timepix3 pixels data. Timepix3 only.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetMeasuredTpx3Pixels(unsigned deviceIndex, Tpx3Pixel* pixels, unsigned pixelCount);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- pixels – pointer to array of Tpx3Pixels that will be filled with measured pixels
- ToT in output data are ToT in 25ns ticks or energy in keVs, depending on Timepix3CalibrationEnabled
- See pxcSetTimepix3CalibrationEnabled, pxcIsTimepix3CalibrationEnabled
- pixelCount – size of the supplied array as number of pixels
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
pxcGetMeasuredRawTpx3Pixels
- Gets the measured Timepix3 pixels data in raw format. Timepix3 only.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetMeasuredRawTpx3Pixels(unsigned deviceIndex, RawTpx3Pixel* pixels, unsigned pixelCount);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- pixels – buffer where pixels will be saved
- pixelCount – size of pixels buffer (number of pixels to save)
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Note
- Use the pxcGetMeasuredRawTpx3Pixels only in special, exceptional cases.
Warning
pxcCalibrateTpx3PixelsAndFilter
- Calibrate the pixel data and filter them by energy range
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcCalibrateTpx3PixelsAndFilter(unsigned deviceIndex, Tpx3Pixel* pixels, unsigned* pixelCount, double minEnergy, double maxEnergy);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- pixels – pointer to array of Tpx3Pixels that will be filled with measured pixels
- pixelCount – size of pixels buffer (number of pixels). It will be filled with the number of pixel remaining after filtration
- minEnergy – minimal allowed energy of each pixel
- maxEnergy – maximal allowed energy of each pixel
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
API frame-data processing functions
Interpolating of bad pixels
pxcInterpolateBadPixels
- Interpolates bad pixels in the image. Uses badPixelsMatrix as bad pixels (badPixel = 1, good = 0)
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcInterpolateBadPixels(unsigned char* badPixelsMatrix, double* data, unsigned width, unsigned height);
Parameters
- badPixelMatrix – matrix of the bad pixels
- data – data to be interpolated
- width – width of the image
- height – height of the image
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
pxcGetDeviceBadPixelMatrix
- Gets the devices's matrix of bad pixels (bad = 1, good = 0). Bad pixels are pixels that are masked.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetDeviceBadPixelMatrix(unsigned deviceIndex, unsigned* badPixelMatrix, unsigned size);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- badPixelMatrix – output data buffer where bad pixel matrix will be saved
- size – size of the data - number of pixels (width * height)
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
Beam hardening correction
The functions described in this chapter can be used to compensate the beam hardening effect, bad pixels and chip sensitivity uneven to get the data with true thickness of measured material.
First step is adding set of the reference images (masks). Dirrect beam (or beam with filter that will be used in all the process) and flat plates with different thicknesses, optimally in whole range that you want measuring. Use the pxcAddBHMask. Reference images contains unsigned 32bit pixels. To create the reference pictures, recommended fold more acquired images to achieve pixel values aproximatelly tens of thousands or more (50,000 is good start). Don’t forget corectly set their thickness.
If 2 or more reference images have been added, it is possible to determine which pixels are not usable. Check this using the pxcGetBHBadPixelMatrix function. If there are too many of these pixels, the pxcApplyBHCorrection function may lose accuracy and the pxcInterpolateBadPixels function will not work. In this case you can check:
- If the set-up is correct (condition of the reference plates; Is the whole area of the chip good irradiated and covered by the reference plates? Is there an obstacle in the beam?)
- If there is too much contrast between the references - a common problem, especially between the free beam and the first reference plate - you can use a filter throughout the process
- If some areas have too low values with high noise - increase the number of integrated frames, beam intensity, or acquisition time
- If exist areas with overexposition – decrease the time or beam intensity
- If the instability of the CdTe chip has manifested itself - increase the time by integrating the reference images
- If using CdTe and measuring start too soon afther chip init
- Try use other beam energy
After add sufficient number of reference images, you can measure image of the sample and use the pxcApplyBHCorrection function. Output is array of double, in units from reference thicknesses.
Now you can use the pxcGetDeviceAndBHBadPixelMatrix to get array of bad and other unusable pixels. Use this data with the pxcInterpolateBadPixels. If it doesn't work, you can use only device bad pixels from the pxcGetDeviceBadPixelMatrix function.
- Example projects
- MiniPixTpx3-Thickness-auto – Acquision time auto tuning for easy first experiments.
- Interactive control in console, text histograms and preview of images. But the code is relatively complex.
- MiniPixTpx3-Thickness-bath – Bath process, using text config file.
- Simple code, but you need to set usable acquisition times.
pxcAddBHMask
- Adds a new mask (frame) for Beam-Hardening calibration.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcAddBHMask(unsigned* data, unsigned size, double frameTime, double thickness);
Parameters
- data – data of the frame tat will be used as BH mask
- size – size of the data - number of pixels (width * height)
- frameTime – acquisition time of the frame in seconds
- thickness – thickness of the measured data
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
pxcBHMaskCount
- Returns number of inserted Beam-Hardening masks (frames)
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcBHMaskCount();
Parameters
- (no pars)
- Return value
- Number of masks if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code
pxcRemoveBHMask
- Removes Beam-Hardening mask (frame)
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcRemoveBHMask(int index);
Parameters
- index – index of the mask to remove
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
pxcApplyBHCorrection
- Applies the Beam-Hardening correction to supplied frame
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcApplyBHCorrection(unsigned* inData, unsigned size, double frameTime, double* outData);
Parameters
- inData – data of the frame that will be corrected
- size – size of the data - number of pixels (width * height)
- frameTime – acquisition time of the measured frame in seconds
- outData – output data buffer where corrected data will be saved
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
pxcGetBHBadPixelMatrix
- Gets the bad pixel matrix from Beam Hardening correction - pixels that cannot be corrected. (bad pixel = 1, good = 0). Must be called after all BH masks are added.
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetBHBadPixelMatrix(unsigned* badPixelMatrix, unsigned size);
Parameters
- badPixelMatrix – output data buffer where bad pixel matrix will be saved
- size – size of the data - number of pixels (width * height)
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
pxcGetDeviceAndBHBadPixelMatrix
- Gets the combined bad pixel matrix from the device and BeamHardening (badpixel = 1, good = 0).
- Definition
PXCAPI int pxcGetDeviceAndBHBadPixelMatrix(unsigned devIndex, unsigned* badPixelMatrix, unsigned size);
Parameters
- deviceIndex – index of the device, starting from zero
- badPixelMatrix – output data buffer where bad pixel matrix will be saved
- size – size of the data - number of pixels (width * height)
- Return value
- 0 if successful, otherwise the return value is a PXCERR_XXX code.
See: pxcGetDeviceBadPixelMatrix, pxcInterpolateBadPixels
Example
See:
Some images
| 1. CdTe 2 mm (left) vs Si 0,3 mm (right)
|
| CdTe disadvantages: Uneven distribution of chip sensitivity. Slow instability can cause the need for a long total measurement time. Specialy thick chips have a easily visible image distortion. Afther start-up, CdTe contains lot of free charges, they can cause problems duringearly measurements (use pxcDoSensorRefresh). |
| 2. The beam hardening experimental setup 1 – The sensor |
| 3. Test images Left is Fe bearing, used reference plates and the setup from img. 2 |
| 4. The Al plates experimental setup
|
The synchronizing
| Sometimes it is necessary to synchronized with an external event. Or some instruments, Widepix-L for example, can be organized as set of more than 1 device in 1 box and more than 1 data cable go out. If you want start acquisition on whole instrument at exactly the same time, must use synchronization by the hardware trigger. |
Synchronizing basics
The acquisition functions have the TrgStg parameter. The 4th argument "trigger settings" of the pxcMeasureTpx3DataDrivenMode(), for example. This have options:
| PXC_TRG_NO | No sync. Normally start immediatelly and stop after acqTime. |
| PXC_TRG_HWSTART | Slave wait and start the acq. on HW signal, master can wait for slave ready. |
| PXC_TRG_HWSTOP |
Start the acq. immediatelly and stop on HW signal or after acqTime. (Available only in specific devices, see sync. manual.) |
| PXC_TRG_HWSTARTSTOP |
Wait and start the acq. on HW signal and stop at next HW signal. (Available only in specific devices, see sync. manual.) |
| PXC_TRG_SWSTART | Wait and start the acq. on SW signal = pxcDoSoftwareTrigger(). |
Additionally, you must use the named parameters. You can read if the device is ready, is it master, etc and write some parameters. Details depends on the device type. Some devices allow reset the ToA counter without restart acquisition or start acquisition without reset the ToA counter.
See: Parameter Get/Set functions (using text paramName)
Synchronizing with an external source
Sync with the external source can depends on the device type. See the synchronization manual of your device type for hardware details.
Example: Way to use the external HW sync with the Advapix-Tpx3
1. Set some synchronization parameters: "TrgTimestamp", "TrgT0SyncReset", "TrgOutLevel", "TrgOutEnable" using function to write the named parameters: pxcSetDeviceParameter.
2. Read some synchronization parameters: "TrgReady", "IsMaster" using the pxcGetDeviceParameter.
3. Start the pxcMeasure... with some PXC_TRG_HW...
4. Apply the sync signal to the input.
Synchronizing in multi-device instruments
(This text is primary about the WIdepix-L with 2 ethernet cables, if using other device, see the Synchronization manual of your device)
Decision which device is master
isMaster = pxcGetDeviceParameter(devIdx, "TriggerMaster");
Output is 0 for slave, 1 for master or single, <0 if the device not supports param name/type.
- Note
- Some devices has IsMaster and some other has TriggerMaster.
- Some devices has output bool (read as int 0/1) and some other has string (read as char[] "Yes"/"No")
- In universal software, expect all 4 combinations to exist.
Master Setup
- Set the parameter TriggerStg = 0
- Set the parameter TriggerWaitForReady = 1
- Set the parameter TriggerOutLevel = 1
Slave setup
- Set the parameter TriggerStg = 2
- Set the parameter TriggerWaitForReady = 1
The measurement
This can be simple if the continuous acquisition is used: This API function starts in separate thread:
rcs = pxcMeasureContinuous(slvIdx, bufCnt, acqTime, PXC_TRG_HWSTART, callback, (intptr_t)slvIdx);
rcm = pxcMeasureContinuous(masIdx, bufCnt, acqTime, PXC_TRG_HWSTART, callback, (intptr_t)masIdx);
errorToList("pxcMeasureContinuous s,m", rcs, rcm);
But if using other acq. functions, you must start slave acq. in separate thread manually.
(see the Visual Studio example “Mpx3-2-sync”)
Note Widepix-L
- If the acquisition time is long, approximately from 100 ms, the run is irregular and there may be long pauses (1 to 5 * acqTime) between acquisitions. This can be suppressed if master acqTime is approximately over 10 % longer.
Widepix-L: The TriggerStg and TriggerOutLevel are linked in the following way:
| Function | Master TriggerStg | Master TriggerOutLevel | Slave TriggerStg | Slave TriggerOutLevel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sync 1:1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | X |
| Alternating sync | 0 | 0 | 2 | X |
| Alternating sync | 0 | 1 | 3 | X |
| Sync 1:1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | X |
X - the value doesn't matter
Synchronizing a multi-device with an external source
Set the device normally for synchronizing in multi-device (See chapter above for details), but in the master settings set the TriggerStg alias TrgStg to 2 or 3 by the used edge of trigger signal. Be carefull if using 0 or 1.
| Function | Master TriggerStg | Master TriggerOutLevel | Slave TriggerStg | Slave TriggerOutLevel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ext and 1:1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | X |
X - the value doesn't matter
Multi-device synchronizing examples
These samples are derived from the Mpx3 project from the AdvacamAPIexamples collection.
Global variables of the example:
unsigned *collectDevFrameD1 = NULL, *collectDevFrameD2 = NULL; // collected devs all frame data
unsigned collectDevFramePxCnt = 0; // collectDevFrameDx size = devWid * devHei * devCnt * collectImgCnt
unsigned devcollectDevsIdx[256]; // list of devs to collect imgs
int collectDevsCnt = -1; // count of devs to be collected (>0 to enable)
int collectDevsMasterIdx = -1; // index of master position in devcollectDevsIdx[]
unsigned collectDevWidth = -1, collectDevHeight = -1; // size of collected image
unsigned collectImgsMax = 0; // =textColImgsMax->Text; vertical count of images to be collected
int collectDevCntCallbacks, collectDevCntOK, collectDevCntFail; // callbacks img collect status
double acqTime = 1.0; // time for acq. functions
int frameCount = 0; // frames count for pxcMeasureMultipleFrames
// or cilcular buffer frames count for pxcMeasureContinuous
int deviceMaxIdx = -1; // maximal connected dev idx (count-1)
int deviceIndex = -1; // index of the single device to be used
int frameLastIndex = -1; // index of the frame that was viewed and for saving
Preparing setup for synchronized Mpx3 multi-device example
Decision if the dev is master (all dev types with internal synchronization):
int isDevMaster(unsigned di) {
int rc = pxcGetDeviceParameter(di, "TriggerMaster");
if (rc == 0 || rc == 1) return rc;
rc = pxcGetDeviceParameter(di, "IsMaster");
if (rc == 0 || rc == 1) return rc;
char val[] = " ";
rc = pxcGetDeviceParameterString(di, "TriggerMaster", val, 4);
if (rc!=0) pxcGetDeviceParameterString(di, "IsMaster", val, 4);
if (rc == 0) {
if (strcmp(val, "Yes") == 0) return 1;
else if (strcmp(val, "No") == 0) return 0;
else return MY_ERR_CODE;
}
return rc;
}
Setup devices, the textCollectDevsOrd contains device indexes order string, like as "102", primary used to joining images side by side in the desired order (Tested with Widepix, ethernet or USB):
collectDevsCnt = textCollectDevsOrd->Text->Length;
int trgMastCnt = 0;
for (int n = 0; n < collectDevsCnt; n++) {
devcollectDevsIdx[n] = Convert::ToInt32(textCollectDevsOrd->Text[n] - '0');
if (devcollectDevsIdx[n] > deviceMaxIdx) { // deviceMaxIdx = global, set after init pxcore
collectDevsCnt = -1;
msgToList(String::Format("Collect devs: devIdx out of range {0}", devcollectDevsIdx[n]));
}
int isMast = isDevMaster(devcollectDevsIdx[n]);
if (isMast < 0) {
errorToList("pxcGetDeviceParameter TriggerMaster", isMast);
isMast = 0;
}
if (isMast == 1) {
trgMastCnt++;
collectDevsMasterIdx = n;
rc = pxcSetDeviceParameter(devcollectDevsIdx[n], "TriggerStg", 0);
errorToList("pxcSetDeviceParameter TriggerStg", rc);
rc = pxcSetDeviceParameter(devcollectDevsIdx[n], "TriggerWaitForReady", 1);
errorToList("pxcSetDeviceParameter TriggerWaitForReady", rc);
rc = pxcSetDeviceParameter(devcollectDevsIdx[n], "TriggerOutLevel", 1);
errorToList("pxcSetDeviceParameter TriggerOutLevel", rc);
} else {
rc = pxcSetDeviceParameter(devcollectDevsIdx[n], "TriggerStg", 2);
errorToList("pxcSetDeviceParameter TriggerStg", rc);
rc = pxcSetDeviceParameter(devcollectDevsIdx[n], "TriggerWaitForReady", 1);
errorToList("pxcSetDeviceParameter TriggerWaitForReady", rc);
rc = pxcSetDeviceParameter(devcollectDevsIdx[n], "TriggerOutLevel", 0);
errorToList("pxcSetDeviceParameter TriggerOutLevel", rc);
}
}
if (trgMastCnt != 1 || collectDevsCnt < 2) {
msgToList("Err: 2 or more devs incl. 1 TriggerMaster needed for collect");
collectDevsCnt = -1;
collectDevsMasterIdx = -1;
} else {
msgToList(String::Format("Collect devs setup complete. Master idx/devIdx:{0}/{1}",
collectDevsMasterIdx, devcollectDevsIdx[collectDevsMasterIdx]));
}
Starting acquisitions for synchronized Mpx3 multi-device example
This section using the callbacks to get actual data. The userData parameter is used to inform the callback function about source device index in the devcollectDevsIdx[]. Based on the index into devcollectDevsIdx[] and the frame index, a place in the buffer is selected and read from the device is called.
Setup and start the synchronized measurement with using continuous acquisition.
Note: Continuous mode is not usable with TDI.
(Tested with Widepix, ethernet or USB):
rc = initMeasParams("Continuous acq. with callback test", true, true); // set-up buffers, operation mode and other measurement settings
if (rc!=0) return;
if (collectDevsCnt > 0) {
for (int n = 0; n <= collectDevsCnt; n++) {
if (n == collectDevsMasterIdx) continue; // skip the master and start it at end
int di = devcollectDevsIdx[n];
if (n == collectDevsCnt) di = devcollectDevsIdx[collectDevsMasterIdx];
rc = pxcMeasureContinuous(di, frameCount, acqTime, PXC_TRG_HWSTART, clbContinuousAcq,
(n < collectDevsCnt) ? n : collectDevsMasterIdx);
msgToList(String::Format("n:{0} di:{1} pxcMeasureContinuous {2} {3}",
n, di, rc, (rc==0)? "OK": "failed"));
if (rc != 0) return;
}
} else {
// pxcMeasureContinuous(unsigned deviceIndex, unsigned frameBufferSize, double frameTime, unsigned trgStg = PXC_TRG_NO, FrameMeasuredCallback callback = 0, intptr_t userData = 0);
rc = pxcMeasureContinuous(deviceIndex, frameCount, acqTime, PXC_TRG_NO, clbContinuousAcq, NULL);
errorToList("pxcMeasureContinuous", rc);
}
Setup and start the synchronized measurement with using multi-acquisition.
A bit more complicated, but works with TDI as well.
(Tested with Widepix, ethernet or USB):
int rc;
DWORD dwThrID;
HANDLE h;
int rc = initMeasParams("More frames with callback test", true, true); // set-up buffers, operation mode and other measurement settings
if (rc!=0) return;
if (collectDevsCnt>0) {
for (int n = 0; n <= collectDevsCnt; n++) {
if (n == collectDevsMasterIdx) continue; // skip master and start it at end
int di = devcollectDevsIdx[n];
if (n == collectDevsCnt) di = devcollectDevsIdx[collectDevsMasterIdx];
sMeasureMultFrsCallbackPars* thrData = new sMeasureMultFrsCallbackPars(di, frameCount, acqTime, PXC_TRG_HWSTART, clbFramesWC,
(n < collectDevsCnt) ? n : collectDevsMasterIdx);
h = CreateThread(NULL, 0, MeasureMultFrsCallbackThrFn, (void*)thrData, 0, &dwThrID);
msgToList(String::Format("n:{0} di:{1} CreateThread {2} OK", n, di, (int)dwThrID));
if (h == NULL) {
msgToList(String::Format("n:{0} di:{1} CreateThread {2} failed", n, di, (int)dwThrID));
return;
}
}
} else {
sMeasureMultFrsCallbackPars* thrData = new sMeasureMultFrsCallbackPars(deviceIndex, frameCount, acqTime, PXC_TRG_NO, clbFramesWC, NULL);
h = CreateThread(NULL, 0, MeasureMultFrsCallbackThrFn, (void*)thrData, 0, &dwThrID);
msgToList("pxcMeasureMultipleFramesWithCallback - thread " + System::Convert::ToString((int)dwThrID));
if (h == NULL) return;
}
Callbacks for synchronized Mpx3 multi-device example
Collecting the image data, called from callbacks (Tested with Widepix, ethernet or USB):
// idx of devcollectDevsIdx, frame idx
void collectDevImgs(unsigned ndi, unsigned fIdx) {
int rc;
size_t adrAdd = static_cast<size_t>(devPixels * (ndi + (fIdx % collectImgsMax) * collectDevsCnt));
unsigned *cd1 = collectDevFrameD1 + adrAdd;
unsigned *cd2 = collectDevFrameD2 + adrAdd;
unsigned bs = collectDevFramePxCnt - adrAdd;
if (bs < 0x80000000) {
rc = pxcGetMeasuredFrameMpx3(devcollectDevsIdx[ndi], fIdx, cd1, cd2, &bs);
} else rc = MY_ERROR_CODE;
collectDevCntCallbacks++;
if (rc == 0) {
collectDevCntOK++;
} else {
collectDevCntFail++;
}
}
The callbacks:
// callback function for "frames with callback"
void clbFramesWC(intptr_t acqCount, intptr_t userData) {
frameLastIndex = acqCount-1;
clbCnt++;
if (collectDevsCnt > 0) {
collectDevImgs((unsigned)userData, frameLastIndex);
return;
}
}
// callback function for continuous acquisition
void clbContinuousAcq(intptr_t acqCount, intptr_t userData) {
if (acqCount<0) {
clbError = acqCount;
return;
}
frameLastDevIdx = (int)userData;
clbCnt++;
if (acqCount<frameCount) {
frameLastIndex = acqCount - 1;
} else {
if (++frameLastIndex>=acqCount) frameLastIndex = 0;
}
if (collectDevsCnt > 0) {
collectDevImgs((unsigned)userData, frameLastIndex);
return;
}
}
Rearranging measured data to complete image
When all measurements are complete, the data is arranged in memory so that each frame from each device occupies a contiguous area. In order for images to be connected when displaying, each line of the resulting image must contain lines from individual neighboring devices.
| Measured data in memory | Rearranged data in memory | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| device 0 / frame 0 | device 0 / frame 0 | device 1 / frame 0 | |
| device 1 / frame 0 | |||
| device 0 / frame 1 | device 0 / frame 1 | device 1 / frame 1 | |
| device 1 / frame 1 | |||
| device 0 / frame 2 | device 0 / frame 2 | device 1 / frame 2 | |
| device 1 / frame 2 | |||
compiledFr1 = (unsigned*)malloc(collectDevFramePxCnt * sizeof(unsigned));
//compiledFr2 = (unsigned*)malloc(collectDevFramePxCnt * sizeof(unsigned));
compiledImgData1 = (int*)malloc(collectDevFramePxCnt * sizeof(int));
//compiledImgData2 = (int*)malloc(collectDevFramePxCnt * sizeof(int));
if (!compiledFr1 || !compiledImgData1) {
msgToList("viewCollectedDevsFrs: Memory allocation failed");
if (compiledFr1) free(compiledFr1);
if (compiledFr2) free(compiledFr2);
if (compiledImgData1) free(compiledImgData1);
if (compiledImgData2) free(compiledImgData2);
return;
}
size_t adrAddIn = 0, adrAddOut = 0;
// adrAdd = devPixels * ndi + collectDevsCnt * devPixels * (fIdx % collectImgsMax);
for (size_t fi = 0; fi < collectImgsMax; fi++) { // frames
for (size_t lin = 0; lin < collectDevHeight; lin++) { // lines of single frame
for (size_t ndi = 0; ndi < collectDevsCnt; ndi++) { // subdevices idxs in collectDevsCnt
adrAddIn = collectDevsCnt * devPixels * fi + devPixels * ndi + devWidth * lin;
if (checkCollectReverseLines->Checked) {
for (size_t x = 0; x < devWidth; x++) {
(compiledFr1 + adrAddOut)[x] = (collectDevFrameD1 + adrAddIn)[devWidth - x];
//(compiledFr2 + adrAddOut)[x] = (collectDevFrameD2 + adrAddIn)[devWidth - x];
}
} else {
memcpy(compiledFr1 + adrAddOut, collectDevFrameD1 + adrAddIn, devWidth * sizeof(unsigned));
//memcpy(compiledFr2 + adrAddOut, collectDevFrameD2 + adrAddIn, devWidth * sizeof(unsigned));
}
adrAddOut += (size_t)devWidth;
}
}
}
colorizeData(compiledFr1, compiledImgData1, collectDevFramePxCnt);
Bitmap^ bmp1c = gcnew Bitmap(collectDevWidth, collectDevHeight * collectImgsMax, collectDevWidth * 4, System::Drawing::Imaging::PixelFormat::Format32bppRgb, (IntPtr)compiledImgData1);
pictureBox3->SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode::StretchImage;
pictureBox3->Image = bmp1c;